Best Unified Endpoint Management Solutions: Top 5 in 2025

What Are Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) Solutions?
Unified endpoint management (UEM) is a security and management solution that provides a single, centralized platform for IT teams to monitor, manage, and secure all of an organization’s end-user devices, including desktops, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices, regardless of their operating system or location.
UEM integrates functionalities from previous systems like Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) to offer a holistic approach, improving visibility, control, and efficiency while reducing complexity and costs for IT departments.
Key features and capabilities of UEM solutions include:
- Centralized device management: UEM provides a single console or dashboard to manage diverse devices, eliminating the need for multiple separate tools.
- Cross-platform compatibility: It secures and manages devices across various operating systems, such as Windows, iOS, and Android.
- Security and compliance management: UEM enforces security policies, monitors devices for threats, and allows for remote device resetting or wiping to protect data.
- Remote monitoring and support: UEM solutions enable IT teams to remotely monitor device health, activity, and compliance status, allowing for proactive issue detection.
- Automation: UEM automates tasks like patch updates, device onboarding, and software deployment, simplifying IT operations and improving productivity.
- Configuration and control: IT teams can deploy configurations, restrict software installations, and ensure compliance with security standards across all endpoints.
This is part of a series of articles about endpoint security
In this article:
Benefits of UEM Solutions
Unified Endpoint Management solutions offer a range of operational, security, and administrative benefits that help organizations manage a growing and diverse fleet of devices. Below are key advantages:
- Centralized management: Manage all endpoints (desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and IoT) from a single platform, reducing the need for multiple tools.
- Improved security posture: Apply consistent security policies, enforce encryption, and remotely wipe compromised devices, minimizing security risks.
- Enhanced compliance: Automate compliance with regulatory standards through policy enforcement, reporting, and audit trails.
- Operational efficiency: Simplify IT operations with automation for device provisioning, software updates, and patch management.
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consolidating management tools into a single solution reduces software licensing, infrastructure, and support costs.
- Lifecycle management: Oversee the entire device lifecycle, from onboarding to retirement, ensuring proper asset tracking and decommissioning.
Key Features and Capabilities of Unified Endpoint Management
Centralized Device Management
Device management in UEM allows IT teams to register, inventory, and monitor different kinds of endpoints regardless of their operating system or manufacturer. Modern UEM platforms support Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and often Linux, which ensures organizations can accommodate a broad fleet of devices. Provisioning, enrolling, and decommissioning devices can be handled remotely, giving IT departments better control during device lifecycle transitions.
Comprehensive device management also encompasses automated configuration, application deployment, and OS patching. This reduces the manual effort needed to keep devices compliant with organizational standards. Security baselines can be established for each device type, ensuring a consistent setup that prevents drift over time, which is critical in maintaining a secure environment.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
UEM platforms are designed to manage and secure a wide variety of operating systems and device types within a single framework. This includes support for Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and increasingly, Linux and ChromeOS. With cross-platform support, IT administrators can apply consistent policies, configurations, and updates across all devices regardless of OS or form factor.
This compatibility ensures uniform visibility and control over both corporate-owned and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) endpoints. It also simplifies policy enforcement and reduces the complexity of managing diverse device ecosystems, particularly in large or global organizations where end-user devices vary widely.
Security and Compliance Management
Security and compliance management is a cornerstone of UEM functionality. Platforms offer encryption enforcement, device compliance checks, and integration with identity and access management systems. These features help protect corporate assets, especially in remote and hybrid work environments.
Compliance dashboards and automated reporting enable audit preparation and regulatory adherence. UEM systems can lock, wipe, or quarantine compromised devices and enforce conditional access based on real-time risk assessments. This helps organizations maintain a strong security posture and respond rapidly to threats or incidents.
Remote Monitoring and Support
UEM solutions provide real-time data streams about endpoint health, status, and user activity. IT teams can see usage trends, flag anomalous behavior, and resolve technical issues without requiring physical access to the device. This ability is particularly valuable for organizations with distributed or remote workforces.
Remote monitoring also enables early threat detection and faster troubleshooting. Many UEM systems integrate remote control tools, letting help desks diagnose and resolve user issues securely over the network. This minimizes downtime and supports consistent device experiences across all user locations.
Automation
UEM systems automate routine IT tasks to reduce manual workload and human error. These tasks include device enrollment, policy enforcement, patch management, software installation, and compliance reporting. Automation helps IT teams maintain a consistent configuration baseline across devices and ensures that critical updates are deployed promptly.
Advanced UEM platforms support conditional logic and event-based automation, such as triggering remediation workflows when a device falls out of compliance. This reduces the time spent on repetitive tasks and allows IT staff to focus on higher-value activities like strategic planning or incident response.
Configuration and Control
Configuration management within UEM systems automates the process of rolling out consistent settings across all endpoints. Whether deploying Wi-Fi credentials, VPN configurations, corporate email profiles, or custom business apps, UEM makes it simple to ensure all users have a standardized setup.
Beyond initial deployment, UEM solutions provide granular control to update configurations as business needs evolve. IT can schedule or trigger changes remotely, manage software inventories, or revoke individual access without interrupting user productivity. This flexibility ensures the endpoint environment stays aligned with changing business requirements.
Limitations of UEM for BYOD Environments
While UEM platforms are designed to manage both corporate-owned and personal devices, their effectiveness in Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) environments can be constrained by privacy and control concerns. Employees often resist device enrollment due to fears that IT will gain access to personal data, messages, or applications. Additionally, organizations may be limited in how aggressively they can enforce policies, such as mandatory encryption or remote wiping, on personal devices without violating privacy laws or user agreements.
Technical and operational challenges can also emerge in BYOD setups with UEM in place. Devices may vary widely in hardware, OS versions, and security posture, making uniform policy enforcement difficult. Fragmented ecosystems can lead to inconsistent app behavior, limited visibility into device compliance, and higher support overhead. In addition, security controls that depend on full device management, like enforcing OS updates or disabling risky configurations, are often unavailable on personal devices. As a result, while UEM improves oversight, it cannot fully eliminate risk in BYOD scenarios.
Better Endpoint Security for Contractors – on Unmanaged Devices
Discover the top solutions for providing secure remote access to contractors on unmanaged laptops. No shipping hardware, no VDI.

Notable Unified Endpoint Management Solutions
1. Venn: UEM Alternative for BYOD

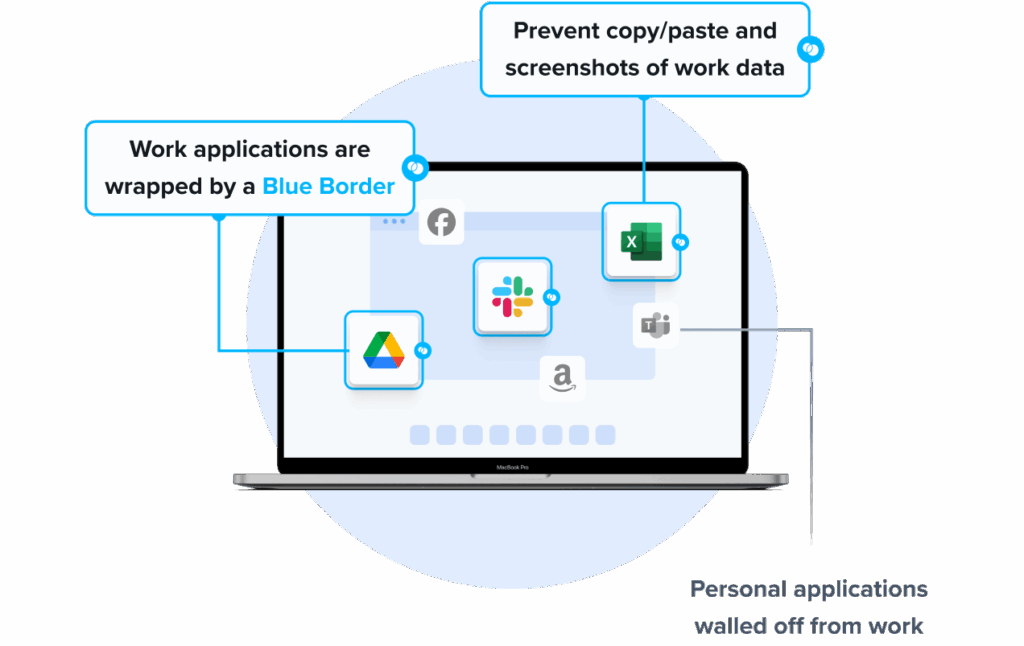
Venn’s Blue Border™ extends enterprise-grade endpoint security to BYOD and unmanaged laptops used by contractors, remote employees, and third-party workers. Unlike traditional UEM solutions, which require full device enrollment, Venn governs only access to sensitive company data and applications through its Secure Enclave: without impacting the device’s configuration. Inside the Enclave, data is encrypted, access is controlled, and work activity is visually separated from personal use, keeping corporate information secure while respecting employee privacy.
Key security controls include:
- Blocking copy/paste between work and personal apps
- Restricting file downloads and use of external storage
- Preventing or watermarking screenshots
- Enforcing consistent protections across both browser-based and local applications
You can book a quick demo here.
2. Workspace ONE

Workspace ONE is a cloud-native UEM solution to consolidate IT operations across device types and use cases. The system helps IT teams eliminate tool sprawl by combining application management, endpoint security, and automation into one interface. With Workspace ONE, organizations can implement zero trust security, automate tasks through IT orchestration, and simplify device lifecycle processes such as onboarding, configuration, and decommissioning.
Key features include:
- Multi-tenant architecture: Define and manage policies at different organizational levels with support for inheritance and overrides.
- IT orchestration and automation: Use low-code tools to automate time-consuming IT tasks such as provisioning, patching, and compliance checks.
- Zero trust security: Continuously assess device and user risk before granting access, and enable automatic remediation or device wipe if needed.
- Remote onboarding and configuration: Provision devices without manual imaging, allowing employees to set up new hardware from any location.
- Lifecycle management: Support application delivery, updates, and decommissioning for all types of apps and devices through a unified app catalog.
Source: Omnissa
3. Citrix Endpoint Management

Citrix Endpoint Management is a unified endpoint management solution to support secure, flexible work across any device and platform. Designed with a strong emphasis on security and compliance, Citrix offers over 300 configurable policies and supports context-aware access to protect corporate data without compromising user experience.
Key features include:
- Multi-platform support: Manage Android (including Samsung Knox), Apple iOS/macOS/iPadOS, and Windows 10/11 devices from one centralized console.
- Cloud and on-premises deployment options: Choose between hosting on-prem or in the cloud, with flexible migration paths that allow seamless transition without user disruption.
- Context-aware security and compliance: Enforce over 300 customizable policies and apply context-based controls such as device posture and risk-level checks to secure access.
- Android Enterprise integration: Separate personal and work profiles on Android devices, allowing IT to manage work-related apps, micro VPNs, and compliance policies without invading user privacy.
- High availability and operational efficiency: Benefit from a 99.9% uptime SLA and offloaded maintenance tasks like updates and monitoring, reducing IT workload.
Source: Citrix
4. Ivanti UEM

Ivanti Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) is a centralized solution that enables IT teams to discover, manage, configure, and secure every type of device from a single console. It supports a range of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, ChromeOS, and rugged and IoT devices, making it adaptable for complex environments.
Key features include:
- Platform coverage: Manage Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, ChromeOS, and IoT devices throughout their lifecycle, from onboarding to decommissioning.
- Automation and self-healing: Use Ivanti Neurons to detect, diagnose, and automatically resolve endpoint issues without user or admin intervention.
- Unified console for full visibility: View and manage all endpoint types from a single interface, enabling faster decision-making and policy enforcement.
- Mobile device management (MDM): Secure and manage mobile endpoints across all major platforms with Ivanti Neurons for MDM, including integration with Android Enterprise and Apple’s enterprise tools.
- Security and compliance controls: Enforce conditional access, encryption, and zero-trust principles while monitoring device compliance.
Source: Ivanti
5. IBM MaaS360

IBM MaaS360 is a cloud-based UEM solution to manage and secure a range of devices, including laptops, desktops, smartphones, tablets, wearables, IoT devices, and purpose-built hardware, from a single console. Delivered as a SaaS platform, it integrates with both cloud and on-premises enterprise systems, offering visibility and control across the endpoint environment.
Key features include:
- Device coverage: Manage and protect major platforms (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Linux, and ChromeOS) plus wearables, IoT, and single-use devices.
- Automation and insights: Leverage Watson-powered analytics to automate risk detection, simplify compliance, and reduce manual IT tasks.
- SaaS architecture: Connect to cloud and behind-the-firewall enterprise resources using the optional Cloud Extender module for seamless integration with systems like Microsoft 365, Azure AD, and file shares.
- Container-based app and data security: Separate personal and work data on mobile devices using secure containers with policy controls, encryption, and SSO support.
- Mobile application management (MAM): Distribute and secure public and in-house apps using the MaaS360 app catalog, Apple VPP integration, and SDK-based app wrapping.
Source: IBM
Related content: Read our guide to unified endpoint management tools (coming soon)
How to Choose UEM Solutions
1. Define Your Business Needs and Goals
Selecting a UEM system begins with a clear understanding of your organization’s requirements. Assess which device types, operating systems, and usage scenarios your environment includes. Consider whether you need to support BYOD, remote work, or regulated data handling, as these will influence the required feature set and compliance controls.
Documenting your security, efficiency, and end user support objectives ensures you shortlist solutions that align with your business priorities. This upfront work minimizes the risk of costly re-evaluations later. Involving stakeholders from IT, security, operations, and compliance will uncover critical needs and improve long-term satisfaction with your chosen platform.
2. Check Ease of Deployment and User Experience
Ease of deployment is crucial for fast UEM adoption and minimal business disruption. Evaluate whether the solution supports automated enrollment, simple configuration, and bulk provisioning. Check for pre-built integrations with your existing infrastructure, such as identity providers or security tools, to simplify setup.
User experience affects productivity and buy-in. A UEM should balance security with usability, avoiding intrusive controls that frustrate users. Test the platform’s administrative interface for clarity and efficiency, and survey end users about their experience with device onboarding, policy enforcement, and troubleshooting workflows.
3. Integration and Ecosystem Compatibility
Assess the UEM solution’s ability to integrate with your current technology stack, including SIEM, IAM, cloud applications, and endpoint security platforms. Compatibility with existing infrastructure allows seamless data exchange and consolidated workflows, reducing silos and duplicate efforts.
Future-proof your investment by evaluating API support, connectors, and documented integration paths. Solutions with broad vendor support enable adoption of new applications or hardware without reengineering management workflows. Ensuring ecosystem compatibility simplifies scaling and adapting to evolving business or regulatory needs.
4. Evaluate Pricing and Licensing Models
UEM pricing structures vary: some are per device, others per user, and some offer tiered or enterprise licensing with bundled features. Assess which model fits your organization’s size, device mix, and growth plans. Consider hidden costs like professional services, training, or premium support that may not be included in base pricing.
Conduct total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis over planned contract periods. Cost-effectiveness should be balanced with feature completeness, scalability, and vendor reputation. Request transparent quotes from shortlisted vendors and clarify which upgrade paths or service add-ons might impact long-term budget planning.
5. Test with a Pilot Program
Running a pilot program is essential before full-scale deployment. Select a representative group of users and devices to validate functionality, performance, and support across your most common workflows. Use this opportunity to verify policy enforcement, integration points, dashboard usability, and support responsiveness from the vendor.
Gather quantitative and qualitative feedback to inform your final selection. Identify any gaps, unexpected blocker issues, or areas requiring customization. A well-structured pilot ensures that when you roll out the UEM platform organization-wide, you have realistic expectations and a smoother implementation process.
Conclusion
Unified endpoint management enables organizations to simplify device oversight, strengthen security, and reduce IT overhead by consolidating endpoint control into a single platform. As enterprise environments become more diverse and distributed, UEM provides the scalability and automation necessary to maintain policy consistency, enforce compliance, and support modern work models. Choosing the right UEM solution involves aligning capabilities with business needs, infrastructure, and long-term goals to ensure effective, sustainable endpoint management across all user devices.