Intune MDM: Pros, Cons, and Top 8 Alternatives in 2025

What Is Microsoft Intune MDM?
Intune MDM is a cloud-based solution from Microsoft for managing and securing mobile devices, PCs, and other platforms like iOS, Android, and Windows. It allows IT administrators to enroll devices, configure settings, enforce security policies (like passcodes and encryption), manage apps, and protect corporate data from a central console.
Intune MDM is part of the unified endpoint management (UEM) capabilities of Microsoft Endpoint Manager, enabling organizations to ensure their devices meet security and compliance standards, whether they are corporate-owned or personal (BYOD) devices.
Key functions of Microsoft Intune MDM include:
- Device enrollment: Users can enroll their devices in Intune, which installs a certificate to enable management and policy enforcement.
- Configuration: IT can create and deploy policies to configure device settings, such as Wi-Fi access, preventing unauthorized connections, and setting up Windows Hello for Business.
- Security & compliance: Intune enforces security measures, ensuring devices meet company standards through features like encryption, passcode requirements, and compliance policies.
- App management: Administrators can install, manage, and update applications on enrolled devices.
- Data protection: Intune helps protect corporate data on devices by managing how devices access it and allowing remote wiping or deletion of organizational data from lost or stolen devices.
- Remote actions: Intune allows for remote management of devices, enabling administrators to lock devices, reset passcodes, perform remote troubleshooting, and wipe devices if necessary.
Secure the Data, Not the Device
Protect company data on unmanaged laptops without locking down the entire device.

In this article:
Key Features and Functions of Microsoft Intune MDM
Device Enrollment
Device enrollment is the first step in bringing endpoints under management with Microsoft Intune MDM. It supports several enrollment methods to handle different scenarios, including automatic enrollment through Azure Active Directory, manual enrollment for BYOD (bring your own device), and bulk enrollment for large device deployments. Each method ensures that devices, whether corporate-owned or personal, adhere to the organization’s management and security requirements as soon as they connect.
Once a device is enrolled, it immediately becomes subject to your organization’s policies and receives relevant configurations, apps, and access controls. This process allows IT teams to maintain visibility over all enterprise endpoints and ensures rapid integration of new devices into the network, but sometimes causes friction among end users.
Configuration
Configuration within Intune MDM enables IT admins to push device settings, network profiles, security parameters, and compliance rules remotely. This can include Wi-Fi and VPN configuration profiles, email account setups, and custom policies tailored to specific departments or device types. Intune’s configuration capabilities are granular, allowing for targeted deployment based on device type, user group, location, or operating system version.
Automated configuration ensures consistency across the device fleet and reduces the risk of human error during manual setup. With the ability to update or revoke settings as requirements change, organizations gain flexibility and control. Intune also permits the scheduling of configuration profiles and policy updates, supporting adaptation to evolving business needs without requiring direct user intervention.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are at the core of Intune MDM’s functionality. The platform allows administrators to define and enforce security baselines across devices, such as password complexity rules, encryption requirements, and device health attestation. Integration with Azure AD Conditional Access strengthens these controls by restricting access to corporate resources based on device compliance status.
Compliance policies play a vital role in risk management, enabling organizations to monitor and remediate non-compliant devices proactively. If a device falls out of compliance due to outdated patches, disabled encryption, or unapproved applications, Intune can automatically trigger actions like sending notifications, restricting access, or remotely locking the device. These capabilities enable enterprises to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive data at scale.
App Management
App management within Intune enables centralized deployment, updating, and removal of applications across all managed devices. Administrators can assign apps as required or optional, target installations by user or device group, and manage app updates without user intervention. The solution supports both store-based and line-of-business apps, offering flexibility for organizations with custom software needs.
Intune provides app protection policies for both MDM-enrolled and unenrolled devices, useful in BYOD scenarios. These policies control data sharing between managed and unmanaged apps, enforce encryption, and restrict copy-paste functions. By managing mobile applications and their interactions, organizations can reduce data leakage risks and ensure that enterprise apps remain secure on user endpoints.
Data Protection
Protecting corporate data on mobile and desktop devices is a priority for organizations, and Intune MDM offers tools to address this. Data protection settings include device encryption, secure access to files, and control over data transfer between business and personal apps. Intune integrates with Microsoft Information Protection to classify and safeguard data based on sensitivity, even at the app level.
Additionally, organizations can implement app-level protections such as requiring authentication to open apps, restricting screenshot capabilities, and monitoring data access in real-time. These measures make it harder for unauthorized users or malicious apps to exfiltrate sensitive information. Together, Intune’s data protection features help organizations maintain compliance and minimize the impact of potential security breaches.
Remote Actions
Microsoft Intune MDM provides a suite of remote actions that enable IT administrators to support, secure, and manage devices without requiring physical access. Key remote actions include device wipe (factory reset), selective wipe (removal of corporate data only), device lock, remote reboot, and password reset. These actions can be executed upon device loss, theft, or compromise to minimize risk and maintain data integrity.
Remote support doesn’t stop at data protection—administrators can also use remote actions to troubleshoot user issues, enforce compliance, or prepare devices for reassignment. By enabling such capabilities through the Intune portal, IT teams can resolve incidents quickly and maintain operational continuity without disrupting end users more than necessary.
Key Limitations of Microsoft Intune MDM
While Microsoft Intune MDM provides capabilities for device and application management, several limitations can affect its usability and efficiency, especially for smaller teams or organizations with non-Microsoft environments. Below are some of the key challenges reported by users on the G2 platform:
- Complex initial setup and steep learning curve: Intune’s extensive configuration options can be difficult to navigate for first-time users. Setting up policies, understanding the interface, and managing hybrid environments often requires prior experience or formal training.
- User interface challenges: The admin portal is divided between legacy and modern experiences, which can confuse new administrators. The interface is also reported to be slow at times, with a vast and sometimes overwhelming set of menus and sub-settings.
- Policy and app sync delays: Updates to policies and application deployments can take considerable time to synchronize across devices. This delay affects real-time visibility and may hinder quick remediation or app rollout.
- Limited reporting without advanced tools: While basic reports are available, advanced reporting capabilities often require external tools like Power BI or use of the Microsoft Graph API, adding complexity for users without those skills.
- Challenges in app deployment: Deploying non-Microsoft Store or custom apps can be tricky. There are also reports of long delays before apps show up in device app collections or during installation.
- Recurring costs for licensing: Intune operates under a subscription model, which may be costly for small to medium-sized businesses, especially when advanced features require higher-tier licenses.
- Integration gaps with other tools: Integration with tools like SCCM for software deployment is not seamless and can cause issues during joint management scenarios or hybrid deployments.
- Slow communication and log collection: The system can be slow in communicating with endpoints, making some administrative actions feel laggy. Collecting system logs and deployment feedback can also take longer than expected.
- Device migration difficulties: Transferring user data and configurations when changing devices, particularly mobile handsets, can be time-consuming and not fully automated, increasing IT support workload.
- Frequent UI and feature changes: Microsoft frequently updates or rebrands features within Intune, which can force administrators to relearn workflows and interfaces they’ve already become familiar with.
Notable Microsoft Intune MDM Alternatives and Competitors
1. Venn

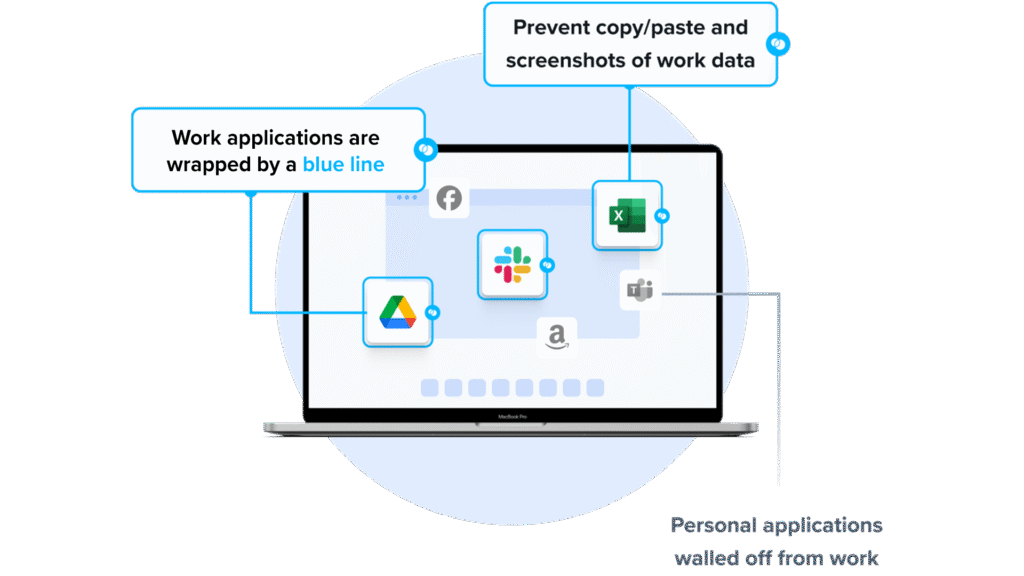
Venn’s Blue Border takes a different path than Intune MDM. Instead of enrolling the entire device, Venn creates a company-controlled Secure Enclave on the user’s laptop, where all data is encrypted and access is managed. Work apps and data run locally inside this protected environment, isolated from any other activity on the device. IT gets the controls required for security and compliance, but only over the enclave — not the user’s personal files, settings, or activity.
This approach removes the source of BYOD friction. With Venn, there is no full-device takeover and no privacy trade-offs. Users keep their laptops the way they like them, while companies get a controlled workspace that safeguards sensitive data and meets regulatory requirements.
Key features include:
- Secure Enclave technology: Encrypts and isolates work data on personal Mac or PC computers, both for browser-based and local applications.
- Zero trust architecture: Uses a zero trust approach to secure company data, limiting access based on validation of devices and users.
- Visual separation via Blue Border: Visual cue that distinguishes work vs. personal sessions for users.
- Supports turnkey compliance: Using Venn helps companies maintain compliance on unmanaged Macs with a range of regulatory mandates, including HIPAA, PCI, SOC, SEC, FINRA and more.
- Granular, customizable restrictions: IT teams can define restrictions for copy/paste, download, upload, screenshots, watermarks, and DLP per user.
2. ManageEngine Endpoint Central
ManageEngine Endpoint Central is an endpoint management solution that competes with Microsoft Intune by offering a set of device, application, and security management capabilities through a unified console. While Intune focuses on integration with Microsoft ecosystems, Endpoint Central emphasizes cross-platform support and operational efficiency, making it suitable for diverse IT environments.
Key features include:
- Unified device management: Supports management of Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android devices from a single console.
- Automated patching: Automatically deploys patches for operating systems and third-party apps across platforms.
- Threat detection and ransomware protection: Provides tools for vulnerability assessment, root cause analysis, and multi-layered endpoint security.
- Mobile device management: Centralizes mobile security, app distribution, content access, and compliance enforcement.
- IT asset management: Tracks hardware and software assets, license usage, and system changes.

Source: ManageEngine
3. Jamf Pro

Jamf Pro is an Apple device management platform built to help organizations manage, secure, and support their macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices at scale. Unlike generalist MDM tools, Jamf Pro is tailored for Apple ecosystems, leveraging native Apple frameworks to deliver an experience for IT administrators and end users.
Key features include:
- Zero-touch deployment: Automatically provisions Mac, iPhone, iPad, and Apple TV devices out of the box using Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager.
- Smart groups: Dynamically groups users or devices based on criteria like location, OS version, or app presence, with support from an AI assistant for faster navigation.
- Blueprints and declarative management: Uses declarative device management to apply configurations, restrictions, and apps efficiently across large fleets.
- Inventory management: Collects real-time hardware, software, and security configuration data for every enrolled Apple device.
- App lifecycle management: Automates app deployment, updates, and removal, ensuring users always have the right tools while reducing IT workload.
Source: Jamf
4. Scalefusion UEM
Scalefusion UEM is a cross-platform unified endpoint management solution that allows organizations to manage and secure devices across Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Linux, and ChromeOS from a single interface. Designed for diverse IT environments, Scalefusion simplifies policy enforcement, app deployment, remote support, and security through a centralized console.
Key features include:
- Multi-OS support: Provides unified management for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and ChromeOS, including specialized support for Android TV and Apple platforms.
- Flexible device management modes: Supports corporate-owned, BYOD, COPE, and kiosk mode deployments to match organizational use cases.
- Automated enrollment options: Offers multiple enrollment methods such as out-of-the-box setup, QR code, serial number, EMM token, and ROM-based provisioning to speed up deployment.
- OS and app update management: Automates operating system and third-party application updates, minimizing vulnerability windows and manual patching overhead.
- Application management: Delivers apps silently from Play Store, App Store, enterprise catalogs, or as PWAs, with options for curated app catalogs and policy-based distribution.
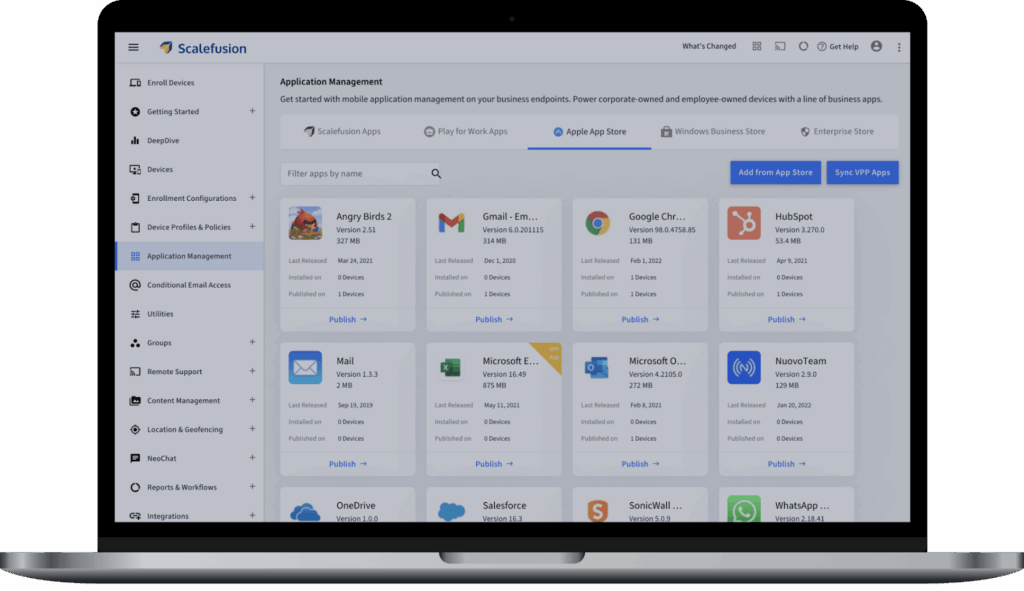
Source: Scalefusion
5. Cisco Meraki MDM

Cisco Meraki Systems Manager (MDM) is a cloud-focused mobile device management solution designed to simplify and secure the management of endpoints across diverse operating systems. As part of the Cisco Meraki ecosystem, it combines device, application, and network security into one platform.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports iOS, macOS, Android, ChromeOS, and Windows devices, enabling centralized control across mobile and desktop endpoints.
- Zero-touch configuration: Automates deployment and policy enforcement at scale, reducing manual setup and speeding up onboarding.
- Integrated network and endpoint security: Works natively with Cisco networking and security products to deliver dynamic, context-aware security policies based on device compliance and network state.
- Automated policy enforcement: Applies security configurations and access rules automatically across thousands of devices with minimal admin effort.
- BYOD and corporate device support: Manages personal and organization-owned devices securely, ensuring policy separation while maintaining user privacy.
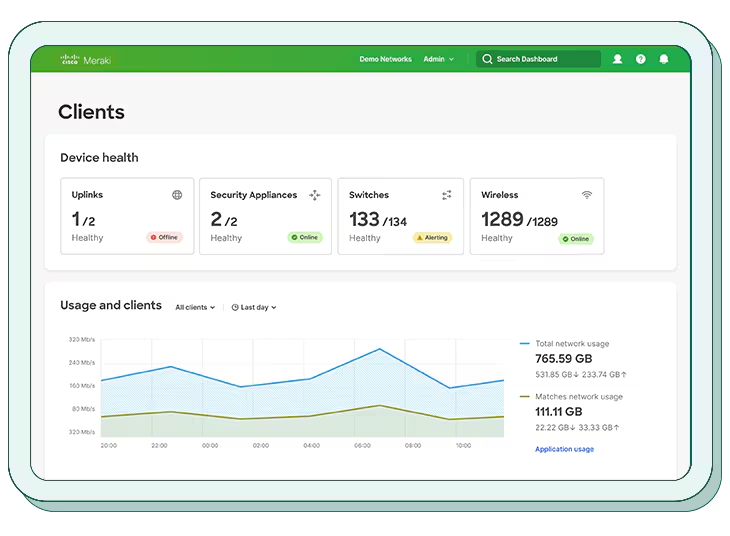
Source: Cisco Meraki
6. IBM MaaS360

IBM MaaS360 is a cloud-based unified endpoint management (UEM) solution to manage and secure a variety of devices including desktops, laptops, smartphones, tablets, wearables, IoT devices, and purpose-built endpoints. Delivered as a SaaS platform on IBM Cloud, MaaS360 supports integration with existing IT systems and security tools, reducing the need for additional investments.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform endpoint management: Supports iOS, Android, Windows, macOS, Linux, and ChromeOS, managing everything from mobile phones to wearables and IoT endpoints.
- SaaS architecture: Cloud-native delivery via IBM Cloud with multi-tenant support and web-based portal access, simplifying deployment and scaling.
- Cloud Extender integration: Connects on-premise resources (like Active Directory and file servers) with cloud-based device management, supporting hybrid environments.
- AI-powered insights: Watson integration provides real-time analytics, risk assessments, and recommended actions to reduce IT workload and enhance security posture.
- BYOD and corporate device support: Offers flexible deployment modes including BYOD, COPE, fully managed, supervised, and kiosk/single-use setups.
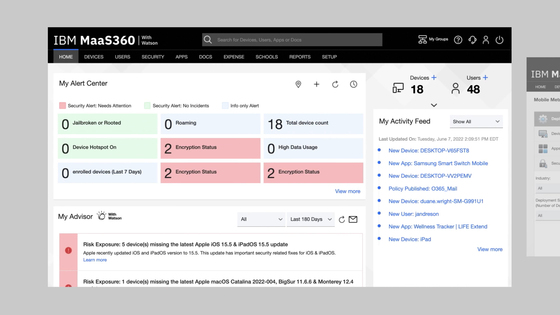
Source: IBM
7. Ivanti MDM

Ivanti MDM is a mobile device management solution to help organizations manage, secure, and scale the use of mobile and desktop endpoints across diverse environments. Part of the Ivanti Neurons platform, it supports BYOD and corporate devices across Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows operating systems.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows endpoints with consistent policy enforcement and configuration management.
- BYOD support: Enables secure access to corporate data from personal devices while maintaining clear boundaries between personal and work content.
- Seamless onboarding: Integrates with Apple Business Manager and Google Zero Touch for automated device provisioning and app deployment.
- Mobile threat defense: Built-in machine learning-based protection runs on-device, detects threats (even offline), and defends against mobile-specific risks like jailbreaking or rooting.
- Application management: Pushes, installs, or removes public and enterprise apps using rules based on user role, device type, or location. Supports Apple VPP and Managed Google Play.
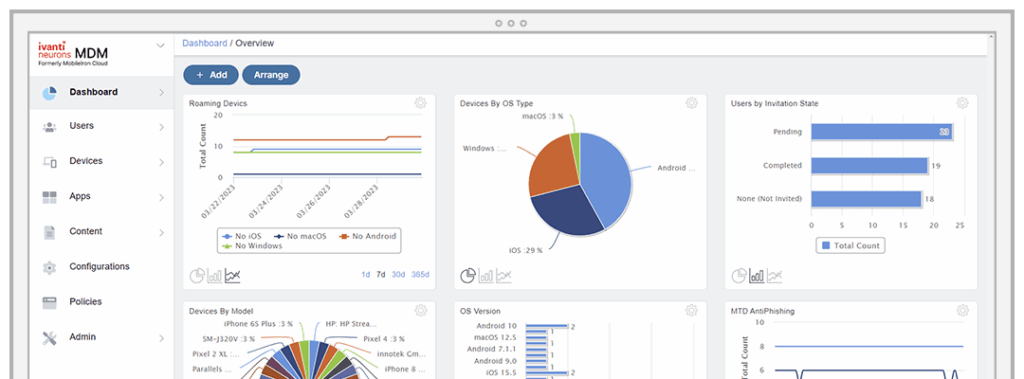
Source: Ivanti
8. 42Gears SureMDM

42Gears SureMDM is a mobile device management (MDM) and unified endpoint management (UEM) platform to help organizations secure, monitor, and control a variety of business endpoints from a single dashboard. Supporting Android, iOS, macOS, Windows, Linux, ChromeOS, VR, Wear OS, and IoT devices, SureMDM enables lifecycle device management.
Key features include:
- Broad platform support: Manages mobile, desktop, wearable, IoT, and rugged devices across Android, iOS/iPadOS, macOS, Windows 10/11, Linux, ChromeOS, VR, and Wear OS.
- Flexible enrollment options: Supports Android Zero-Touch, Apple Business Manager, Windows Autopilot, and manual or app-based enrollment for corporate or BYOD setups.
- Provisioning and app deployment: Pushes apps from Managed Google Play and Apple Business Manager or provides access to an enterprise app store and secure file store.
- Kiosk mode and lockdown tools: Includes SureLock to restrict devices to single or multiple approved apps, and SureFox for safe, limited browsing environments.
- Deployment automation: Installs security certificates and manages Wi-Fi access post-deployment, even when settings are locked down on the device.
Source: 42Gears
Conclusion
Organizations evaluating MDM solutions must balance security, flexibility, user experience, and ecosystem alignment. While some platforms focus on deep integration with specific operating systems, others offer broad cross-platform coverage and advanced UEM features. The right choice depends on device diversity, regulatory needs, IT maturity, and whether the organization prioritizes full device control or prefers a more lightweight, app-focused approach to endpoint security.