BYOD Tools: Top Categories and Best 5 Tools in 2025

What Are BYOD Tools?
There are several categories of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) tools including secure enclave technology, Mobile Device Management (MDM), Unified Endpoint Management (UEM), Network Access Control (NAC), and other security solutions that enable organizations to configure, monitor, and secure personal devices for business use, manage access to corporate resources, and enforce compliance with security policies.
Popular examples of BYOD management tools include Venn, Citrix Endpoint Management, and Microsoft Intune.
A typical BYOD solution provides mechanisms for controlling access policies, monitoring device compliance, and segregating organizational data from users’ personal information. They are crucial in modern workplaces that support remote and hybrid work models, as they defend against threats that emerge when unmanaged devices connect to sensitive infrastructure.
In this article:
Core Functions of BYOD Tools
Application Management and Sandboxing
BYOD tools enable IT teams to control which applications can be installed, accessed, and executed on a user’s device while connected to corporate networks. Application management frequently utilizes blacklisting and whitelisting to ensure only approved software runs during work sessions. Features like mobile application management (MAM) isolate work apps from personal ones, reducing risk from malicious or vulnerable third-party apps.
Sandboxing takes application management a step further by confining the operation of work applications to a secure, controlled environment on the device. This separation restricts data flow between corporate and personal apps, ensuring sensitive information remains protected even if a user’s device becomes infected with malware.
Data Protection and Encryption
A central pillar of BYOD security is protecting organizational data through encryption at rest, in transit, and in use. BYOD tools enforce encryption policies for files, emails, and app data, even when these reside on a user’s personal device. File containers, secure mail clients, and managed app workspaces shield business information from exposure.
Beyond encryption, capabilities like data loss prevention (DLP) limit users’ ability to copy, share, or upload work information outside approved channels. Automated data wiping can quickly remove corporate data if a device is lost or an employee leaves the company. These protective features ensure sensitive data does not leak due to loss, theft, or improper use of personal devices.
Remote Monitoring and Device Lifecycle Management
Remote monitoring functionality allows IT administrators to track device compliance, location, installed apps, and health in real time. Continuous monitoring is vital for early detection of suspicious behavior, policy violations, or emerging security threats. BYOD tools present this data through dashboards and automated alerts, simplifying risk management across a dynamic fleet of devices.
Device lifecycle management extends from initial enrollment to decommissioning, ensuring proper onboarding, policy enforcement, and secure data removal at the end of employment or device use. By automating processes such as software updates, access revocation, and remote wipe, organizations can maintain security standards while reducing administrative overhead.
Device Enrollment and Authentication
Device enrollment is the process by which a personal device is registered and approved for access to corporate resources. During enrollment, the device’s identity, operating system, and security posture are vetted, and appropriate policies are enforced. Authentication mechanisms, such as certificates or multifactor authentication, ensure only authorized devices and users are granted access. This foundational function creates a trust boundary between the user’s device and organizational networks.
A robust enrollment process also involves periodic checks to ensure continued compliance, automatically revoking access if a device becomes compromised or fails to meet policy guidelines. Secure authentication helps protect against credential theft, unauthorized usage, and lateral attacks within the network.
Secure Network Access Control
Secure network access control limits device access based on predefined criteria, such as user roles, device compliance status, or geographic location. BYOD tools can integrate with network security systems to limit what enrolled personal devices can see and do on the corporate network. This reduces risk exposure by segmenting traffic and restricting access to only the resources necessary for a user’s job function.
Network access control also employs dynamic policy enforcement, adapting access permissions in real time based on device health or detected threats. Features like network quarantining, guest VLANs, and contextual access reviews minimize the attack surface presented by personal devices.
Types of BYOD Tools
Secure Enclave Technology
A secure enclave is a hardware-based trusted execution environment that isolates work-related data and applications from the rest of a personal device. Secure enclaves enable organizations to protect sensitive information in bring your own device (BYOD) settings while preserving user privacy and minimizing administrative overhead.
The secure enclave creates a partitioned workspace where only company-managed apps and data reside. This prevents unauthorized access between personal and corporate content, reducing the risk of privilege escalation, data leakage, and zero-day attacks. Work-related files are stored on an encrypted virtual drive, inaccessible from outside the enclave, and supports copy/paste restrictions, screen capture prevention, and device peripheral limitations.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Mobile device management (MDM) platforms give IT administrators control over mobile devices connecting to the corporate network, regardless of ownership. Through centralized consoles, admins enforce policies on device configuration, security settings, connectivity, and permitted apps. MDM features typically include remote lock, wipe, GPS tracking, and root/jailbreak detection, supporting compliance and rapid incident response in case of device loss or compromise.
MDM platforms are crucial in organizations where varied mobile operating systems and device models are present, as they centralize policy enforcement and simplify user support. By separating personal and work environments on the same device, MDM solutions balance user privacy with organizational security needs.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
Unified endpoint management (UEM) extends the scope of MDM to include all endpoint types (laptops, desktops, smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices) under one management platform. UEM offers policy orchestration, compliance checks, and visibility across an organization’s device landscape. This consolidation simplifies management overhead and minimizes gaps caused by having siloed tools for different platforms.
UEM solutions are valuable in large or hybrid organizations seeking to enforce uniform policies and respond to threats, regardless of device form factor or operating system. By integrating inventory, patch management, access control, security policy, and compliance reporting for all endpoints, UEM simplifies IT processes and improves the organization’s security posture.
Mobile Application Management (MAM)
Mobile application management (MAM) tools focus on managing and securing the applications and data on user-owned devices, as opposed to the devices themselves. MAM works by wrapping or containerizing enterprise apps, implementing encryption, user authentication, and policy controls at the software level. This ensures that sensitive data accessed via mobile apps is protected even on unmanaged devices.
MAM is useful for organizations that want to allow BYOD without imposing broad device-wide controls. It gives IT teams precise control over app usage, enables secure updates, and supports selective data wipe when necessary. With MAM, organizations can enforce data leakage prevention measures and maintain productivity without infringing on employees’ personal app environments.
Network Access Control (NAC)
Network access control (NAC) solutions authenticate and evaluate devices at the point of network connection, enforcing security policies before granting access. NAC can inspect device posture, patch level, and compliance status, allowing or denying connectivity based on risk. This prevents non-compliant or unauthorized devices from threatening network resources.
NAC tools provide granular segmentation, guest access management, and real-time enforcement of network security rules. Integration with BYOD policies strengthens defenses at the point where most ransomware and malware attacks attempt initial infiltration.
Enable Remote Workers Without VDI or Issuing Devices
Unlock the 4 essential assets you need to secure company data on unmanaged laptops – without VDI.

Integrating BYOD Tools with Enterprise Systems
Here are a few ways BYOD tools work together with other parts of the enterprise IT stack.
Integration with Active Directory and SSO
Integrating BYOD tools with Active Directory (AD) enables centralized user identity management and access control across all devices. By linking device enrollment and authentication to AD, IT can automate permissions, enforce group policies, and onboard users efficiently. Connecting BYOD solutions with single sign-on (SSO) further simplifies authentication, letting users access multiple work applications with a unified set of credentials.
This integration produces stronger security and improved user experience, reducing password fatigue and simplifying account lifecycle management. With AD and SSO integration, organizations can also use conditional access rules, ensuring only compliant devices and users gain entry to sensitive resources.
Cloud-Based Management and Scalability
Cloud-based BYOD management platforms allow IT teams to oversee device security and compliance remotely, regardless of user location. Moving management to the cloud reduces reliance on internal infrastructure, enabling faster onboarding, centralized policy updates, and real-time visibility. This approach supports organizations with distributed workforces or those adopting remote and hybrid work models.
Scalability is inherent to cloud solutions, letting enterprises add or remove devices and users seamlessly as needs change. Updates, patches, and feature rollouts occur automatically, minimizing manual intervention and downtime. Cloud-based management also improves disaster recovery and business continuity by ensuring continuous access to administrative functions offsite.
API and Automation Capabilities
Modern BYOD solutions offer extensive APIs that let organizations automate tasks, integrate with IT service management (ITSM) tools, and orchestrate complex workflows. APIs enable custom integrations with ticketing systems, incident response platforms, and business apps, aligning BYOD tool operations with broader enterprise processes. This interoperability is critical for supporting scalable and agile IT operations.
Automation simplifies repetitive processes, such as user onboarding, policy enforcement, compliance audits, and remediation of non-compliant devices. By leveraging APIs and automation, organizations can reduce human error, accelerate response times, and lower support costs.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
BYOD environments feature a broad array of operating systems, device models, and form factors. Cross-platform compatibility ensures BYOD tools can enforce consistent policies and deliver unified user experiences regardless of whether employees use Windows, iOS, Android, or macOS devices. This is vital for organizations with diverse technology stacks and variable employee preferences.
Supporting multiple platforms helps minimize application compatibility issues, reduces IT support queries, and future-proofs investments as new devices emerge. Cross-platform BYOD tools ensure consistent security, reporting, and compliance across the enterprise.
Notable BYOD Tools
1. Venn

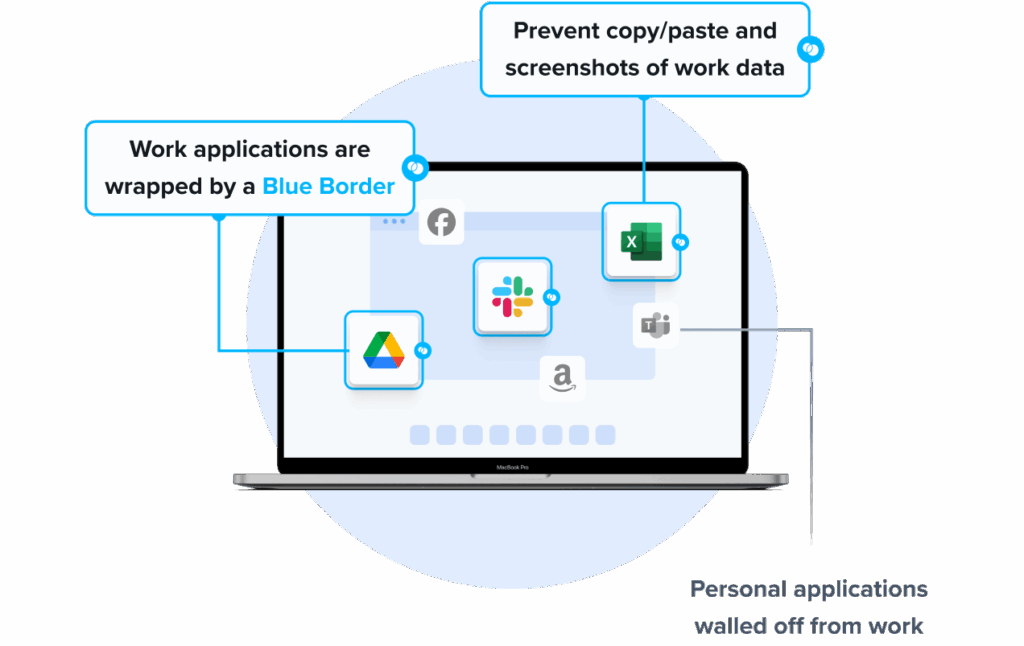
Venn’s Blue Border was purpose-built to protect company data and applications on BYOD computers used by contractors and remote employees.
Similar to an MDM solution but for laptops, work lives in a company-controlled Secure Enclave installed on the user’s PC or Mac, where all data is encrypted and access is managed. Work applications run locally within the Enclave – visually indicated by Venn’s Blue Border™ – protecting and isolating business activity while ensuring end-user privacy. With Venn, you can eliminate the burden of purchasing and securing laptops and managing virtual desktops (VDI).
Key features include:
- Secure Enclave technology: Encrypts and isolates work data on personal Mac or PC computers, both for browser-based and local applications.
- Zero trust architecture: Uses a zero trust approach to secure company data, limiting access based on validation of devices and users.
- Visual separation via Blue Border: Visual cue that distinguishes work vs. personal sessions for users.
- Supports turnkey compliance: Using Venn helps companies maintain compliance on unmanaged Macs with a range of regulatory mandates, including HIPAA, PCI, SOC, SEC, FINRA and more.
- Granular, customizable restrictions: IT teams can define restrictions for copy/paste, download, upload, screenshots, watermarks, and DLP per user.
2. Citrix Endpoint Management

Citrix Endpoint Management is a unified endpoint management platform that provides both mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) capabilities, helping organizations secure and control user access to corporate data on personal devices. It supports policy enforcement, app delivery, identity management, and encryption across endpoints while offloading infrastructure responsibilities to Citrix Cloud Operations.
Key features include:
- MDM and MAM: Centralized control over device and application policies for secure, consistent management across mobile and desktop endpoints
- Micro VPN integration: Provides secure per-app VPN tunnels, especially when used alongside Intune-aware apps like Microsoft Edge
- Conditional access with Azure AD: Allows access control to Office 365 and corporate resources based on device and user posture
- Cloud connector architecture: Enables secure communication with on-prem resources without requiring VPNs or complex infrastructure changes
- Granular policy enforcement: Supports device-level quarantine, selective app blocking, and ActiveSync customization
Source: Citrix
3. Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution that provides tools to manage and secure personal (BYOD) and organization-owned devices. While control of software updates on unmanaged personal devices is limited, Intune offers multiple policy-based methods to guide and enforce compliance.
Key features include:
- Enrollment restrictions: Define minimum and maximum OS versions to block noncompliant personal devices during the enrollment process
- Work profile management: Automatically applies a work profile to Android BYOD devices, ensuring organizational policies stay isolated from personal data
- Compliance policies: Mark devices as noncompliant if they don’t meet OS version requirements, and trigger actions such as user warnings or grace periods
- Conditional access integration: Combine compliance policies with Azure AD conditional access to block access to corporate resources until compliance is achieved
- App protection policies: Apply OS and patch version checks at the app level for unmanaged devices, prompting or blocking access based on policy settings
Source: Microsoft
4. LogMeIn Resolve

LogMeIn Resolve is a UEM platform that brings together remote monitoring, asset management, automation, and support into a single solution for managing both personal and organization-owned devices. Resolve helps IT teams secure, maintain, and support a range of endpoints, including Windows, Mac, and Android, while integrating with existing tools.
Key features include:
- Mobile device management: Enforce endpoint compliance, optimize performance, and protect company data across BYOD and corporate devices using scalable MDM capabilities
- Remote monitoring and management: Continuously monitor endpoints with automated patching, alerting, antivirus integration, and performance tracking through a centralized console
- Unattended remote access: Resolve user issues and perform maintenance on BYOD devices even when they’re offline, enabling seamless support across diverse environments
- IT asset management: Track software and hardware inventory, enforce license compliance, and simplify asset lifecycle decisions for better control and visibility
- Service management tools: Includes built-in ticketing, knowledge base, and problem resolution features to simplify IT workflows and improve support response times
Source: Resolve
5. Hexnode UEM

Hexnode UEM is a unified endpoint management platform that supports centralized management of diverse devices across multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and ChromeOS. Hexnode helps organizations simplify onboarding, enforce security, deploy updates remotely, and automate routine tasks.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, Linux, ChromeOS, Fire OS, tvOS, and VisionOS devices from a unified interface
- Zero-touch deployment: Simplifies onboarding of personal and corporate devices with silent or guided setup flows, including support for Windows Autopilot and Automated Device Enrollment for macOS
- Remote configuration and scripting: Apply settings, restrictions, and custom scripts to individual devices or groups without physical access
- Patch and Update Management: Push OS updates, patches, and app updates over the air to ensure security and performance consistency across devices
- Hexnode gateway and access: Securely migrate devices to Hexnode with or without user interaction and enable cloud-based credential login policies for Windows systems
Source: Hexnode
Conclusion
BYOD tools are essential for securing enterprise data in environments where personal devices are used for work. They provide the visibility and control needed to manage diverse device types, enforce policy compliance, protect sensitive information, and respond to security incidents.
Whether managing access, isolating corporate data, or automating security operations, these tools help organizations maintain a strong security posture without compromising user productivity or privacy. When selecting and implementing BYOD solutions, aligning them with existing infrastructure and operational goals ensures effective risk mitigation and seamless integration into broader IT strategies.