Browser Security Tools: Key Features and Top 13 Options in 2026

What Are Browser Security Tools?
There are several types of browser security tools, including remote work solutions like Venn, browser security platforms like LayerX, dedicated enterprise browsers like Island, browser security extensions like those offered by MalwareBytes, and private browsers like Brave.
These tools address vulnerabilities in browsers, which are frequent targets for attack due to their role in accessing the internet. By providing layered defenses, they aim to prevent exploits, mitigate risks from malicious web content, and ensure safer browsing for users and organizations.
Browser security solutions go beyond traditional antivirus or simple web filters. They integrate protection directly into the browser or operate in tandem with it, focusing on shielding critical data, detecting threats in real time, enforcing security policies, and protecting privacy. Such measures are crucial in environments where browsers serve as gateways to sensitive resources, cloud applications, and corporate data.
Go Beyond the Browser. Secure All Apps.
Learn how Venn secures both browser-based AND locally installed apps on unmanaged devices.

In this article:
Types of Browser Security Tools
Remote Work Security Platforms
Remote work solutions like Venn focus on separating work and personal browser environments, especially on BYOD devices. They often enforce data boundaries using virtualization or secure containers, ensuring that enterprise data cannot leak through personal browsing activities. These platforms integrate with identity providers and endpoint security tools to maintain compliance and data integrity outside corporate networks.
Dedicated Enterprise Browsers
Dedicated enterprise browsers like Island are designed with built-in controls that align with corporate security policies. Unlike traditional browsers, they come pre-integrated with DLP, identity management, and content inspection tools. These browsers offer native support for role-based access, secure copy-paste restrictions, and detailed session recording to reduce insider threats.
Browser Security Extensions
Browser security extensions from providers like Malwarebytes add a security layer on top of standard browsers. These lightweight tools offer features such as ad blocking, phishing protection, malicious site detection, and real-time tracking prevention. They are easy to deploy and maintain, making them a quick win for enhancing user security on unmanaged or lightly managed devices.
Private Browsers
Private browsers such as Brave are designed to minimize data exposure by default. They block trackers, fingerprinting scripts, and unwanted cookies without requiring additional configuration. These browsers also limit how much personal data websites can collect, supporting privacy-focused browsing for individuals and organizations concerned about surveillance and behavioral profiling.
Key Features of Browser Security Tools
Sandboxing and Site Isolation
Sandboxing is a defense in browser security, segregating browser processes so that malicious code cannot escape one tab or session to affect the entire device. When sandboxes are implemented, each website runs in its own restricted environment, curbing the impact of harmful scripts or infected web applications. This compartmentalization prevents lateral movement, reducing the risk that attackers can exploit browser vulnerabilities to access sensitive local files or installed applications.
Site isolation ensures that each site a user visits is rendered in a separate process. This approach is effective against attacks like Spectre and Meltdown, which target browser memory and data leaks between sites. By enforcing strict process boundaries between domains, site isolation adds another layer of defense, limiting the opportunity for one compromised site to jeopardize others or expose cross-site data.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Policy Enforcement
Real-time threat detection is central to modern browser security, employing AI-driven analytics and signature-based heuristics to spot malicious content as users browse. These mechanisms analyze web pages, scripts, and downloads in real time, instantly blocking known threats and flagging suspicious behaviors. By dynamically updating based on global threat intelligence feeds, security solutions ensure users are protected against emerging attack methods without frequent manual intervention.
Policy enforcement features enable organizations to define acceptable use rules and enforce them consistently across all users. This can include restrictions on file downloads, copy-paste actions, and navigation to specified URL categories. When policy violations are detected, administrators receive alerts and can take immediate remedial action. Such capabilities are key to limiting data exposure and ensuring adherence to regulatory or organizational requirements.
Anti-Phishing and Anti-Malware
Anti-phishing modules examine URLs and website contents to detect fraudulent attempts at credential theft. These systems work by cross-referencing links against constantly updated threat databases and analyzing page structures for phishing indicators. When users attempt to access suspicious sites, the solution intervenes to block access or display warnings, minimizing the risk of compromised accounts and stolen information.
Similarly, anti-malware capabilities scan downloads and browser-based file transfers for malicious payloads. Leveraging malware engines, these security tools can identify both known and zero-day threats before they reach the endpoint. Integration with browser download workflows ensures threats are intercepted immediately, bolstering user defense against ransomware, spyware, and other pervasive browser-delivered attacks.
Strict Content Security Policies (CSP)
Implementing content security policies (CSP) is a core feature of browser security. CSPs help restrict what types of content can be loaded by a browser from which sources, reducing the risk from cross-site scripting (XSS) and data injection attacks. These policies are configured to limit the execution of untrusted scripts, prevent the loading of dangerous resources, and curb the impact of vulnerabilities in third-party plugins or extensions.
Administrators may leverage CSP enforcement to mandate HTTPS usage, block inline scripts, and tightly restrict resource domains. Such control is vital for organizations that rely heavily on SaaS or web-based applications, ensuring that only sanctioned content is rendered and that attempts to exploit content injection flaws are thwarted at the browser level.
Granular Governance and Access Control
Granular governance tools provide detailed oversight of user activity within the browser, enabling organizations to prioritize least-privilege access. These features support custom access controls that define which applications, data, or services can be reached, and by whom. By implementing adaptive authentication and access monitoring, IT teams can quickly identify anomalous behavior and respond to potential account compromise.
Access control also extends to auditing browser activity for investigative or compliance purposes. Solutions routinely log events such as attempted downloads, failed logins, or visits to restricted URLs. This visibility aids incident response and simplifies reporting for regulatory frameworks, including GDPR or HIPAA, which demand clear records of sensitive data handling.
Privacy Protection
Browser security tools enforce privacy protection by controlling how user data is collected, stored, and transmitted. They can block third-party cookies, obfuscate digital fingerprints, and limit browser telemetry shared with websites. This reduces the ability of advertisers, data brokers, or malicious actors to track users across the web.
Some tools go further by supporting features like ephemeral browsing sessions, automatic history wiping, or isolated user profiles. These capabilities are especially useful in regulated industries or when accessing sensitive internal systems, where minimizing data residue and exposure is essential.
Notable Browser Security Solutions
Remote Work Security Platforms
1. Venn

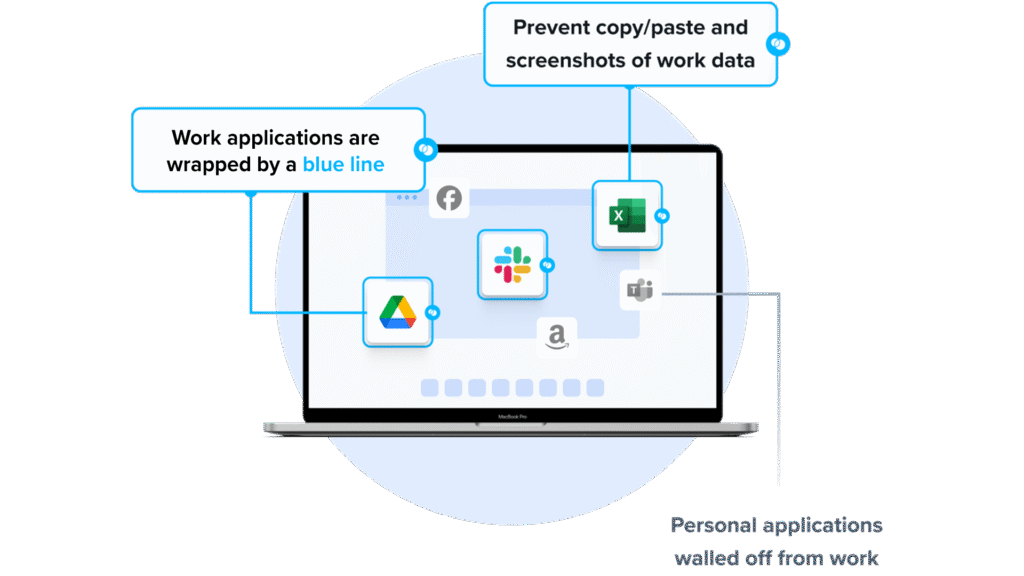
Venn’s Blue Border was purpose-built to protect company data and applications on BYOD computers used by contractors and remote employees.
Similar to an MDM solution but for laptops, work lives in a company-controlled Secure Enclave installed on the user’s PC or Mac, where all data is encrypted and access is managed. Work applications run locally within the Enclave – visually indicated by Venn’s Blue Border™ – protecting and isolating business activity while ensuring end-user privacy. With Venn, you can eliminate the burden of purchasing and securing laptops and managing virtual desktops (VDI).
Key features include:
- Supports turnkey compliance: Using Venn helps companies maintain compliance on unmanaged Macs with a range of regulatory mandates, including HIPAA, PCI, SOC, SEC, FINRA and more.
- Granular, customizable restrictions: IT teams can define restrictions for copy/paste, download, upload, screenshots, watermarks, and DLP per user.
- Secure Enclave technology: Encrypts and isolates work data on personal Mac or PC computers, both for browser-based and local applications.
- Zero trust architecture: Uses a zero trust approach to secure company data, limiting access based on validation of devices and users.
- Visual separation via Blue Border: Visual cue that distinguishes work vs. personal sessions for users.
2. Seraphic Security

Seraphic Security provides in-browser protection by operating inside the browser’s JavaScript engine (JSE). Unlike endpoint detection and response (EDR), secure service edge (SSE), or browser extensions that operate on the periphery, Seraphic’s approach embeds an abstraction layer inside the JSE.
Key features include:
- In-JSE protection: Operates inside the JavaScript engine to detect and block threats invisible to traditional endpoint or network-based tools.
- Universal deployment: A single lightweight agent covers corporate, third-party, and mobile devices, working across all major browsers and platforms.
- Execution context visibility: Provides inspection of browser operations at runtime, enabling real-time threat detection and policy enforcement.
- Extension-based for corporate devices: Delivered via lightweight browser extensions for seamless deployment, no separate agents or user interaction required.
- Embedded for third-party devices: Turns the browser into a secure environment for accessing corporate resources.
Source: Seraphic Security
3. LayerX Security

LayerX Security transforms a standard browser into a secure enterprise workspace by embedding monitoring and enforcement capabilities directly into the browsing environment. Delivered as a lightweight browser extension, LayerX analyzes web sessions down to granular elements.
Key features include:
- Web session analysis: Monitors every browser interaction, such as page content, file activity, and user inputs, to detect and stop threats at the point of use.
- Adaptive policy enforcement: Enforces risk-based policies based on user identity, device posture, application type, and data sensitivity, with actions ranging from monitoring to blocking.
- Complete visibility: Provides insight into identities, accounts, applications, and user behavior across all browsers to eliminate blind spots.
- User activity tracking: Captures user actions including text input, copy/paste, downloads, uploads, printing, and cookie usage for auditing and threat detection.
- Cross-browser support: Compatible with all major chromium- and mozilla-based browsers, allowing enterprises to secure existing browser environments without requiring users to switch.
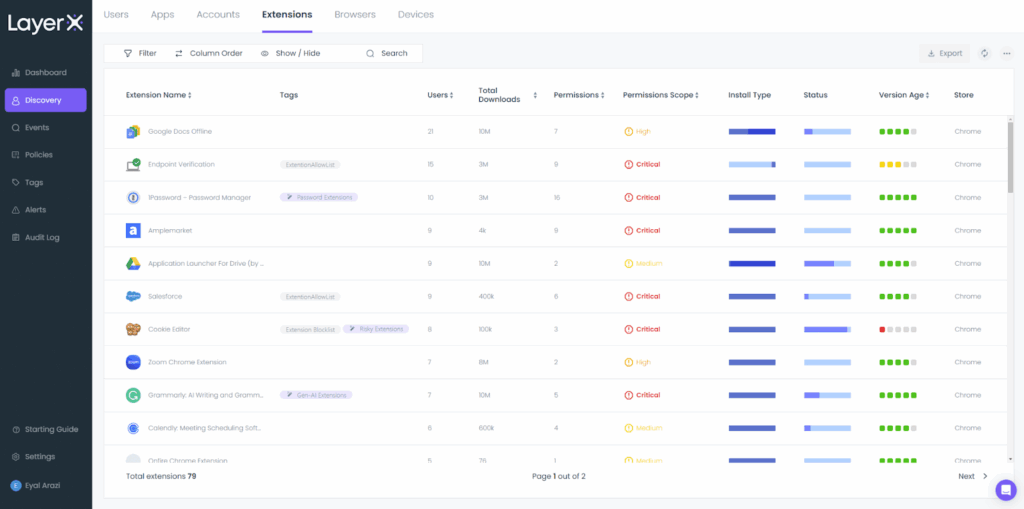
Source: LayerX
Dedicated Enterprise Browsers
4. Island

Island is a secure enterprise browser that embeds security and control directly into the browsing environment. Instead of relying on external add-ons or third-party tools, Island builds these protections into the browser itself, creating a manageable workspace for enterprise users. It enables secure access to applications while preventing phishing, malware, and data leakage.
Key features include:
- Built-in security controls: Security functions such as data loss prevention and malware blocking are natively integrated, eliminating the need for separate tools.
- Secure app access: Ensures safe and policy-driven access to enterprise applications, reducing exposure to untrusted networks or endpoints.
- Support for BYOD: Allows secure browsing from personal devices by enforcing enterprise policies without impacting user privacy or device control.
- Third-party onboarding: Enables fast, controlled access for contractors and external partners, minimizing provisioning time and complexity.
- Phishing and malware protection: Automatically blocks known threats and suspicious activity to keep users and data safe.
Source: Island
5. Chrome Enterprise

Chrome Enterprise adds centralized management and security controls to the Chrome browser. Organizations can manage policies across platforms, with Chrome Enterprise Core for no-cost management and Chrome Enterprise Premium for advanced protections and data controls.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform browser management: Configure policies, settings, apps, and extensions from a cloud console, regardless of operating system, device type, or location.
- Reporting and insights: Get fleet-wide reporting on versions, apps, extensions, and security events to inform updates, audits, and incident investigations.
- Advanced security (Premium): Add real-time safe browsing, deep file scanning, DLP, URL filtering, and evidence locker for stronger browser-level protections.
- Context-aware access: Restrict access to SaaS, Google Cloud, and private web apps based on user, location, and device security posture.
- Extension governance: Review requests and permissions, then manage allowed extensions centrally to reduce risk from unvetted add-ons.
- On-prem alternatives: Use ADM/ADMX templates with Active Directory for environments requiring group policy–based, on-premises browser management.
Source: Google Chrome
6. Microsoft Edge for Business

Microsoft Edge for Business is an enterprise browser with native integrations across Entra ID, Purview, Defender for Endpoint, and Intune. It applies zero trust principles, supports BYOD, and embeds AI features while maintaining organizational controls.
Key features include:
- Identity-aware security: Enforce policies with Entra ID sign-in, applying device health checks and protections across managed and personal devices.
- Built-in management: Use the Edge management service to configure policies, manage extensions, and monitor versions directly in Microsoft 365 admin.
- Integrated Microsoft 365: Provide access to work resources and services, aligning browsing with existing productivity tools and governance.
- AI assistance with Copilot: Integrate AI into workflows for summaries and guidance, with organizational data protections enforced by platform integrations.
- Mobile support: Extend protections to iOS and Android for secure connectivity in flexible work and BYOD scenarios across smartphones and tablets.
- Legacy app support: Configure IE mode for sites requiring Internet Explorer, reducing disruption while transitioning to modern web standards.

Source: Microsoft
7. Palo Alto Prisma Access Browser

Prisma Browser is a secure enterprise browser from Palo Alto Networks, natively integrated with Prisma SASE. It extends SASE protections to managed and unmanaged devices, providing a secure workspace with browser-level visibility and control. Use cases include securing independent workers, BYOD access, governing GenAI application usage, and reducing dependence on VDI.
Key features include:
- SASE-native integration: Natively integrated with Prisma SASE, extending network and data protections to the browser across managed and unmanaged devices with consistent enforcement.
- Zero trust access and controls: Apply zero trust access policies and granular data controls to secure remote access for independent workers, contractors, and BYOD scenarios.
- Managed and unmanaged device coverage: Provide a secure workspace and consistent policy enforcement on corporate endpoints and personal devices, supporting secure remote access for independent workers and BYOD environments.
- GenAI usage governance: Gain visibility into activity within GenAI applications to protect enterprise data and block unsanctioned “shadow AI” usage at the browser level.
- VDI reduction option: Offer a browser-centric approach that can reduce reliance on traditional VDI by enabling secure access to applications through policy-driven controls.
Source: Palo Alto Networks
Browser Security Extensions
8. Malwarebytes

Malwarebytes is a cybersecurity vendor focused on protecting users and organizations from online threats. The source link references the vendor’s security offerings without detailing a specific browser extension or feature set.
Key features include:
- Vendor-provided threat protection: Offers security products designed to detect and block malware and related web threats across supported environments.
- Consumer and business focus: Serves individuals and organizations with solutions intended to improve protection against prevalent online risks.
- Product information at source: Directs administrators and users to the vendor site for current product capabilities, platforms, and deployment guidance.
- Evolving capabilities: Indicates ongoing development and updates; consult the source for the latest features, integrations, and availability details.
Source: Malwarebytes
9. Privacy Badger

Privacy Badger is a browser extension from the Electronic Frontier Foundation that automatically learns and blocks third-party trackers based on behavior. It sends Global Privacy Control and Do Not Track signals and enforces them algorithmically.
Key features include:
- Behavior-based blocking: Identifies third-party domains tracking across sites and blocks them automatically without relying solely on static blocklists.
- GPC and DNT signaling: Sends Global Privacy Control and Do Not Track signals, then restricts domains that ignore consent and continue tracking users.
- Cookie and referrer controls: Uses a “yellowlist” mode to allow required functionality while stripping third-party cookies and referrers from necessary domains.
- Tracker widget handling: Replaces social widgets and embedded content with click-to-activate placeholders to prevent passive tracking until user consent.
- First-party protections: Removes outgoing link click tracking on platforms like Facebook and Google to reduce additional tracking vectors.
- Enterprise deployment: Provides documentation for managed deployments and configuration, supporting administration at scale in enterprise environments.
10. Ghostery

Ghostery provides privacy tools including a tracker and ad-blocking extension, a private search engine, and transparency resources. It focuses on blocking hidden trackers, minimizing ads, and surfacing tracker information to users.
Key features include:
- Tracker and ad blocking: Blocks hidden trackers, removes intrusive ads, and prevents cookie pop-ups to reduce profiling and improve page experiences.
- Anti-tracking measures: Neutralizes trackers by stripping personal identifiers, replacing them with random values to limit downstream data collection.
- Private search engine: Offers ad-free private search with tracker information displayed alongside results, independent of major ad networks.
- Transparency with WhoTracks.Me: Publishes tracker research informing protections and enabling users to understand data-sharing practices.
- Multi-browser support: Provides extensions across major browsers and platforms to standardize protections in varied user environments.
Source: Ghostery
Private Browsers
11. Brave Privacy Browser

Brave is a privacy-focused browser with built-in tracking protections, ad blocking, and additional services. It includes a private search engine, integrated VPN and firewall, and an AI assistant accessible within the browser.
Key features include:
- Default tracker blocking: Blocks third-party ads and trackers by default across sites, reducing profiling and improving page load performance.
- Cookie pop-up handling: Suppresses or auto-handles cookie consent dialogs where possible to minimize interruptions during browsing sessions.
- Private search integration: Uses Brave Search for private queries with zero profiling, emphasizing results over ad targeting or personalization.
- Built-in VPN and firewall: Offers device-wide protection via a bundled VPN and firewall service to secure network traffic beyond the browser.
- Integrated AI assistant: Provides the Leo AI assistant for answers and content tasks directly inside the browser interface.
- Enterprise controls: Supports enterprise group policy installation to customize enabled features for organizational deployments.
Source: Brave
12. DuckDuckGo

DuckDuckGo offers a privacy-centric browser and search engine designed to limit data collection. It blocks third-party trackers and most ads, handles cookie pop-ups, and provides cross-platform apps and extensions.
Key features include:
- Tracker and ad blocking: Blocks third-party trackers from major platforms and most ads by default to reduce surveillance and bandwidth usage.
- Cookie consent management: Detects cookie pop-ups and opts out where possible to minimize prompts and background data collection.
- YouTube without targeted ads: Plays videos without targeted advertising to reduce profiling while preserving core functionality.
- Built-in password manager: Includes a simple password manager to store credentials locally within the browsing environment.
- Private AI chat (optional): Enables private chats with popular AI chatbots without linking activity to personal identities or accounts.
- Cross-platform availability: Provides browsers for Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android, with extensions for major desktop browsers.
Source: DuckDuckGo
13. Epic Privacy Browser

Epic Privacy Browser is a Chromium-based browser emphasizing privacy protections. It blocks ads, trackers, fingerprinting, and other tracking methods, with additional features like an encrypted proxy and WebRTC leak prevention.
Key features include:
- Tracker blocking: Blocks ads, third-party cookies, fingerprinting techniques, cryptomining, and ultrasound signaling to limit pervasive web tracking.
- Encrypted proxy / VPN: Includes an encrypted proxy with country selection to hide IP addresses and unblock content subject to regional restrictions.
- WebRTC leak prevention: Prevents IP leaks through WebRTC calls, addressing a common privacy gap not covered by standard private modes.
- Chromium foundation: Uses a Chromium codebase for performance and security while removing data collection and profiling practices.
- History minimization: Deletes local browsing history on close and isolates tabs as separate processes to reduce residual data exposure.
- Extension compatibility: Supports most Chrome Web Store extensions, allowing customization without ceding core privacy protections.
Source: Epic Browser
Learn more in our detailed guide to browser security solutions
Evaluation Criteria for Browser Security Solutions
Choosing the right browser security solution requires evaluating how well a tool aligns with an organization’s security, usability, and operational requirements. The following criteria help assess the effectiveness and practicality of these tools:
- Deployment model: Consider whether the solution is delivered as a standalone browser, an extension, a remote isolation platform, or a centralized management tool. The deployment model affects compatibility, ease of rollout, and integration with existing infrastructure.
- Threat coverage: Evaluate the range of threats the solution addresses, such as phishing, malware, data leakage, XSS, and token theft. A solution should offer both signature-based detection and behavioral analysis.
- Visibility and control: Assess the level of user activity monitoring, policy enforcement, and governance features. Solutions should allow real-time insights and control over web sessions, data interactions, and application access.
- Performance impact: Measure the effect on browser speed and user experience. Solutions that introduce high latency or interfere with normal workflows may reduce user compliance and productivity.
- Compatibility and integration: Ensure the solution works across multiple browsers, devices (including BYOD), and integrates with identity providers, endpoint security tools, and SIEM platforms.
- Policy flexibility: Look for granular, identity-aware policies that adapt to context, such as user role, device posture, or application sensitivity. This is crucial for enforcing least-privilege access.
- Scalability and manageability: Consider the administrative effort needed to deploy, configure, and maintain the solution at scale. Centralized dashboards, API support, and remote configuration capabilities are important for large or distributed environments.
- Regulatory compliance support: Verify that the solution provides features like audit logging, data protection, and access controls to support compliance with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
- Vendor support and roadmap: Evaluate the vendor’s support model, frequency of updates, and roadmap for addressing emerging browser threats and compliance needs.
Learn more in our detailed guide to browser security solutions
Conclusion
Browser security solutions aid in protecting users and organizations against web-based threats that traditional endpoint defenses often miss. By combining techniques such as sandboxing, isolation, real-time detection, and granular policy enforcement, these tools provide layered protection at the browser level where most attacks originate. Selecting the right solution ensures safer access to applications and data, reduces the risk of breaches, and supports compliance requirements in increasingly cloud-driven and distributed environments.