Top 10 Mobile Device Management Solutions and Alternatives in 2026

What Are Mobile Device Management (MDM) Solutions?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions are security and management software platforms that enable organizations to centrally monitor, secure, and enforce policies on mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops connecting to their network. By centralizing device administration, MDM solutions allow IT teams to protect sensitive corporate data, regardless of whether devices are corporate-owned or employee-owned (BYOD).
MDM solutions typically cover smartphones, tablets, and laptops across iOS, Android, and Windows platforms. They provide centralized dashboards for device tracking, software distribution, configuration updates, and real-time policy enforcement.
Common MDM features include:
- Remote device actions: Lock, wipe, or reset devices remotely.
- Policy enforcement: Push out mandatory security and usage policies across all managed devices.
- App management: Distribute, update, and manage internal and third-party applications.
- Asset management: Track device inventory and usage.
- Remote troubleshooting: Remotely diagnose and resolve device issues.
In this article:
Core Capabilities of Mobile Device Management Solutions
1. Remote Device Actions
Remote device actions are a foundational capability of modern MDM platforms. These actions allow administrators to lock, wipe, or locate devices in the event of loss or theft, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. For example, if a phone containing company data is lost, IT teams can remotely erase its content or disable it entirely to prevent data leaks.
Beyond security measures, remote actions facilitate device initialization and troubleshooting without requiring physical access to the hardware. Administrators can initiate device restarts, push configuration changes, or reset passwords remotely, reducing downtime and enhancing the organization’s ability to maintain a secure and consistent mobile environment.
2. Policy Enforcement
Policy enforcement is central to MDM solutions, enabling organizations to specify, deploy, and monitor compliance with device policies. Policies can dictate password requirements, data encryption, app installation restrictions, or network usage guidelines. MDM platforms ensure these rules are applied uniformly across all managed devices, reducing the likelihood of security gaps that could arise from inconsistent configurations or user behavior.
Continuous monitoring allows IT teams to detect and remediate policy violations in real time. Non-compliant devices can be quarantined, have restricted network access, or receive remediation prompts automatically. This proactive enforcement ensures that all devices maintain a prescribed security baseline, supporting regulatory compliance efforts and reinforcing the organization’s overall data protection posture.
Learn more in our detailed guide to BYOD policy
3. App Management
App management is another significant feature of MDM solutions, enabling administrators to control which applications can be installed, updated, or removed on managed devices. This includes distributing authorized business apps, blocking unapproved software, and patching vulnerabilities by ensuring apps are up to date. MDM solutions often include enterprise app stores, where users can find pre-approved applications tailored to their roles.
Effective app management reduces the threat surface by restricting the introduction of potentially harmful or unvetted software. It also streamlines the user experience by centrally distributing productivity tools and automating app updates. By managing the app lifecycle, organizations minimize security risks and help users remain productive without jeopardizing sensitive business information.
4. Asset Management
Asset management capabilities within MDM solutions give organizations visibility into their device fleet. Administrators can access detailed inventories, view device status, operating system versions, and installed applications. This data is crucial for planning upgrades, tracking hardware refresh cycles, and ensuring that unsupported or outdated devices are identified and either updated or retired as needed.
In addition to managing hardware and software inventories, asset management features can monitor device usage statistics and network activity. These insights help organizations optimize resource allocation, enforce cost controls, and align their technology investments with evolving business needs. Asset tracking also supports compliance audits and loss prevention initiatives by ensuring every device is accounted for throughout its lifecycle.
5. Remote Troubleshooting
Remote troubleshooting is a valuable MDM capability that allows IT teams to diagnose and resolve device issues without requiring in-person intervention. Through remote access tools, administrators can view device status, analyze logs, and initiate corrective actions such as rebooting or reconfiguring settings. These features are particularly useful in distributed organizations with a large number of remote or field employees.
Effective remote troubleshooting minimizes device downtime and user frustration, while also reducing support costs by minimizing the need for physical device handling or shipping. Quick problem resolution keeps employees productive and ensures critical devices remain operational.
Are MDM Solutions Suitable for a Modern BYOD Environment?
Traditional MDM solutions are often not well-suited to modern BYOD environments because they depend on full-device control, which conflicts with the personal nature of employee-owned devices. Enrolling a personal phone or laptop in an MDM program grants IT administrators broad access, potentially including visibility into installed apps, device configurations, and usage data. This raises privacy concerns and often leads to user resistance or noncompliance.
From a technical perspective, MDM platforms struggle to maintain consistent control across diverse devices and operating systems. Variations in hardware, OS versions, and manufacturer restrictions can limit enforcement of security policies like encryption, password complexity, or app blocking.
MDM also focuses on securing the device rather than the data or applications themselves. Once corporate data is accessible on a personal device, it becomes difficult to isolate and protect it without disrupting personal use. These limitations make MDM inefficient, intrusive, and unreliable for securing modern BYOD environments, which increasingly require app- and data-centric security approaches instead of device-level management.
Related content: Read our guide to BYOD security
Enable Remote Workers Without VDI or Issuing Devices
Unlock the 4 essential assets you need to secure company data on unmanaged laptops – without VDI.

MDM Alternatives for BYOD Environments
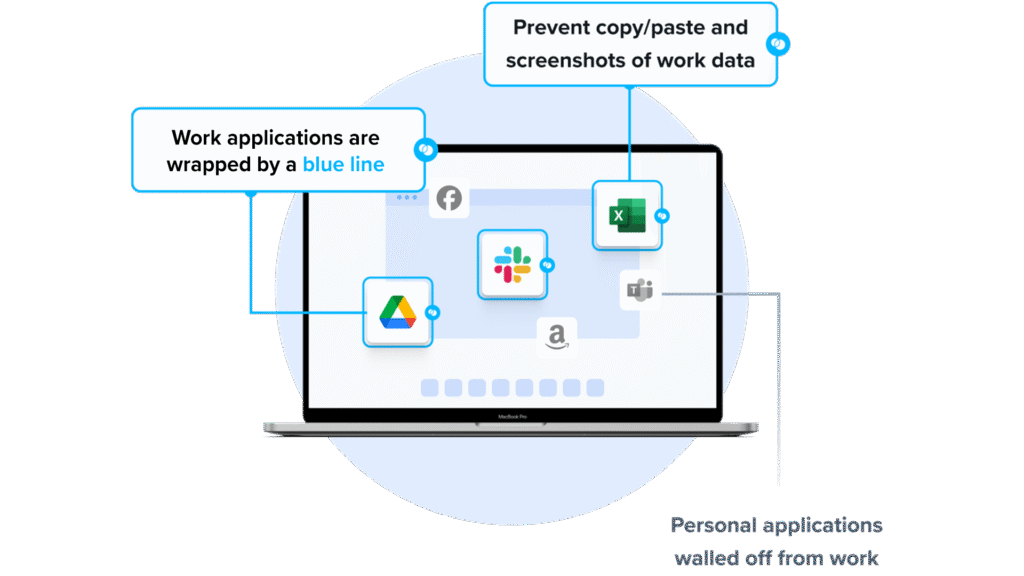
1. Venn’s Blue Border

Venn’s Blue Border was purpose-built to protect company data and applications on BYOD computers used by contractors and remote employees.
Similar to an MDM solution but for laptops, work lives in a company-controlled Secure Enclave installed on the user’s PC or Mac, where all data is encrypted and access is managed. Work applications run locally within the Enclave – visually indicated by Venn’s Blue Border™ – protecting and isolating business activity while ensuring end-user privacy. With Venn, you can reap the benefits of MDM technology without the drawbacks of full-device control.
Key features include:
- Supports turnkey compliance: Using Venn helps companies maintain compliance on unmanaged Macs with a range of regulatory mandates, including HIPAA, PCI, SOC, SEC, FINRA and more.
- Granular, customizable restrictions: IT teams can define restrictions for copy/paste, download, upload, screenshots, watermarks, and DLP per user.
- Secure Enclave technology: Encrypts and isolates work data on personal Mac or PC computers, both for browser-based and local applications.
- Zero trust architecture: Uses a zero trust approach to secure company data, limiting access based on validation of devices and users.
- Visual separation via Blue Border: Visual cue that distinguishes work vs. personal sessions for users.
2. Duo Premier

Duo Premier is an MDM alternative that emphasizes policy-driven access and centralized administration. It aligns device usage with defined security baselines through remote actions, compliance controls, app governance, asset visibility, and remote troubleshooting.
Key features include:
- Remote device actions: Lock, wipe, or disable devices when lost or stolen, and push configuration changes or password resets without requiring physical access.
- Policy enforcement: Define and apply password, encryption, and app restrictions uniformly; quarantine or limit access for noncompliant devices until remediation occurs.
- App management: Distribute approved applications through managed catalogs, restrict unapproved software, and automate updates to reduce vulnerability exposure across personal endpoints.
- Asset management: Maintain device inventories, OS versions, and installed apps to plan upgrades, retire unsupported hardware, and align spending with usage patterns.
- Remote troubleshooting: Diagnose issues via logs and remote tools, initiate reboots or configuration changes, and restore access quickly for distributed employees and contractors.
Source: Duo
3. Zscaler CASB

Zscaler CASB focuses on governing data and application use across devices. It enforces standardized policies, manages application availability and updates, and supports remote response and diagnostics for distributed users.
Key features include:
- Centralized policy enforcement: Apply device and application rules for passwords, encryption, and network usage, with continuous monitoring and automated remediation for violations.
- Application governance: Publish approved apps, block unapproved software installations, and enforce timely updates using enterprise catalogs to limit exposure to known vulnerabilities.
- Remote response actions: Remotely lock, wipe, or disable compromised devices, and push configuration updates to restore compliant states without on-site intervention.
- Fleet visibility: Track device inventories, software versions, and activity to support audits, plan refresh cycles, and identify unsupported or risky configurations.
- Remote diagnostics: Use remote access capabilities to analyze logs, adjust settings, and resolve issues for distributed users, minimizing downtime and support overhead.

Source: Zscaler
Traditional Mobile Device Management Solutions
4. IBM MaaS360

IBM MaaS360 is a cloud-based unified endpoint management (UEM) solution that provides centralized control over mobile devices, desktops, laptops, and other endpoints across an organization. Delivered as a SaaS platform, MaaS360 supports a wide range of operating systems including iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS.
Key features include:
- Unified endpoint management (UEM): Manages mobile devices, desktops, laptops, IoT, and purpose-built devices from a single console
- SaaS-based architecture: Hosted on IBM Cloud with multi-tenant support and a centralized web portal
- Cloud Extender integration: Connects with Active Directory and behind-the-firewall systems for seamless access and identity management
- AI-powered insights: Uses IBM Watson for threat detection, remediation, and reducing administrative workload
- Secure container architecture: Separates personal and business data on mobile devices using a workplace container and enterprise apps
Source: IBM
5. Microsoft Intune

Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution that enables organizations to manage, secure, and configure a range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktops. Integrated with Microsoft Entra ID, Intune uses policy-based controls to protect both organizational data and access across personal and corporate-owned devices.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Supports Android, iOS/iPadOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux devices
- Unified admin center: Central portal to manage policy deployment, device configuration, compliance monitoring, and remote actions
- Flexible enrollment options: Enrolls both organization-owned and personally owned (BYOD) devices, with support for app-only management
- Compliance policies and conditional access: Enforce minimum OS versions, password rules, firewall settings, and more; block access for noncompliant devices
- Device configuration controls: Manage built-in features like camera access, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi settings
Source: Microsoft
6. ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus

ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus is a unified endpoint management solution to secure and manage smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktops, rugged devices, and smart TVs across various platforms, including Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Chrome OS, and tvOS. Available as both cloud-based and on-premises deployments, it offers a centralized console for IT teams to handle device provisioning, policy enforcement, and app management.
Key features include:
- Broad platform support: Manages Android, iOS, iPadOS, macOS, Windows, Chrome OS, and tvOS devices from a single dashboard
- Flexible enrollment: Supports easy onboarding of both BYOD and corporate devices with secure authentication and provisioning workflows
- Centralized dashboard: Provides an overview of device status, compliance, and app usage with a central interface
- Real-time device management: Remotely control and troubleshoot devices, perform remote locks, wipes, and view device screens
- App management: Distribute, update, and restrict both in-house and public apps across all major platforms; supports kiosk mode for single/multi-app lockdown
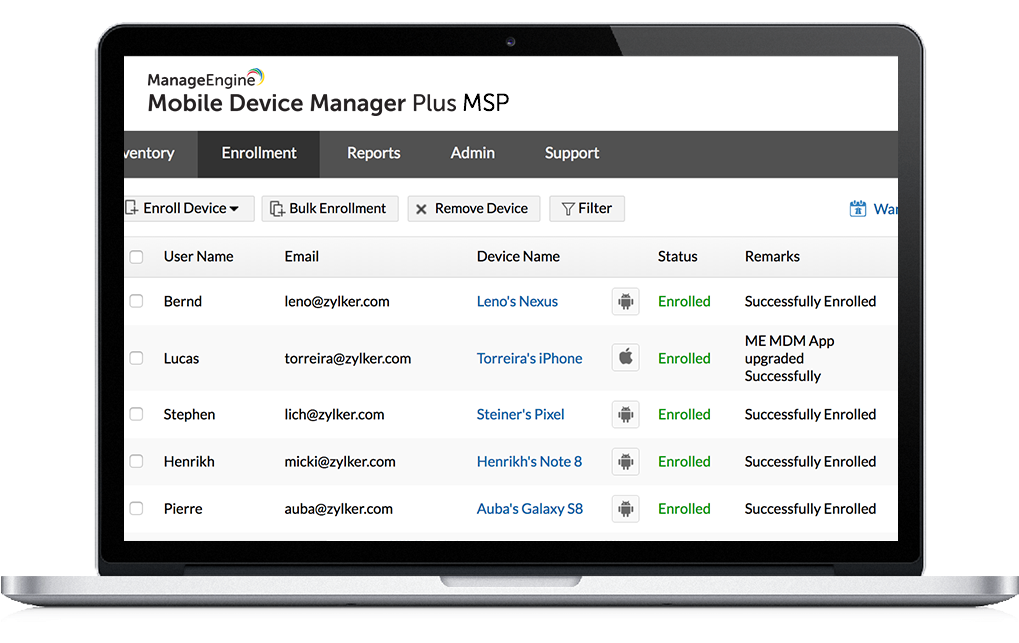
Source: ManageEngine
7. Jamf

Jamf is an MDM solution for managing Apple ecosystems: macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices. Unlike cross-platform MDM tools, Jamf leverages Apple’s native frameworks to offer deep configuration, seamless deployment, and strong security integration. It supports zero-touch enrollment through Apple Business Manager and School Manager, allowing devices to be automatically configured and secured.
Key features include:
- Apple-first design: Tailored to fully support Apple’s native capabilities for device management, configuration, and security
- Zero-touch deployment: Automates device setup through Apple Business Manager and School Manager; users just open the box and log in
- Same-day OS support: Ensures compatibility and security on the day of each new Apple OS release, reducing downtime and patch delays
- Security and compliance: Supports CIS benchmarks and compliance reporting; includes Apple-based threat intelligence and natural language policy queries
- App management: Remotely deploys, updates, and patches App Store, third-party, and custom applications
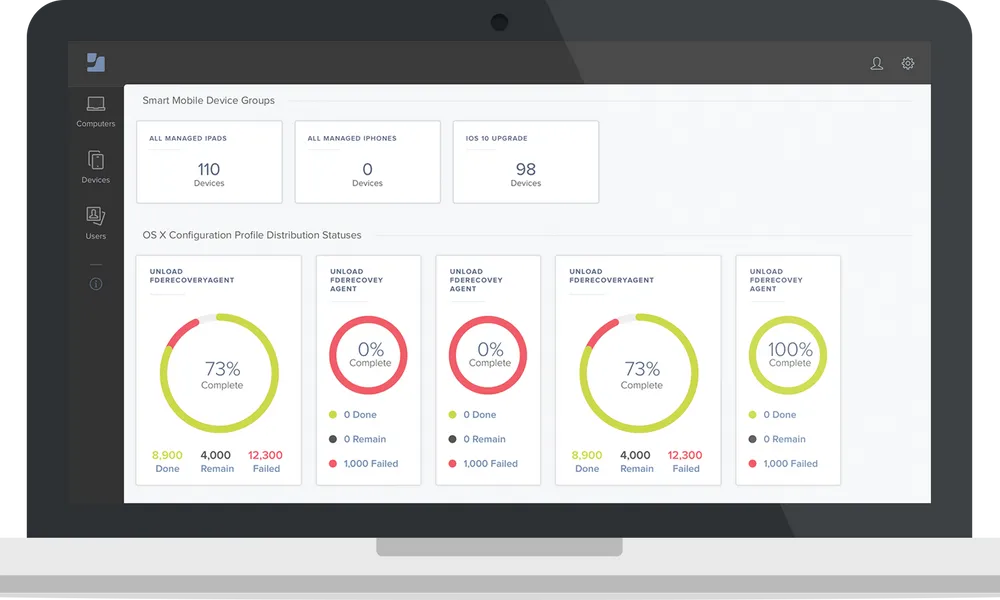
Source: Jamf
8. Miradore

Miradore is a cloud-based MDM solution to help small and medium-sized businesses manage Android, Apple, and Windows devices through a single platform. Developed by LogMeIn (GoTo), Miradore enables IT teams to enroll, configure, and secure devices, with automation tools that simplify routine tasks and reduce manual errors.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform management: Supports Android, iOS/iPadOS, macOS, and Windows devices from a unified interface
- Quick start and simplicity: Easy setup process allows companies to begin managing devices in minutes
- Security and compliance: Enforces safe passcodes, encrypts data, restricts unauthorized apps, and separates work and personal use
- Remote configuration: Install device settings, deploy updates, and manage configurations without physical access
- Application management: Control which apps can be installed or used, and block unwanted applications
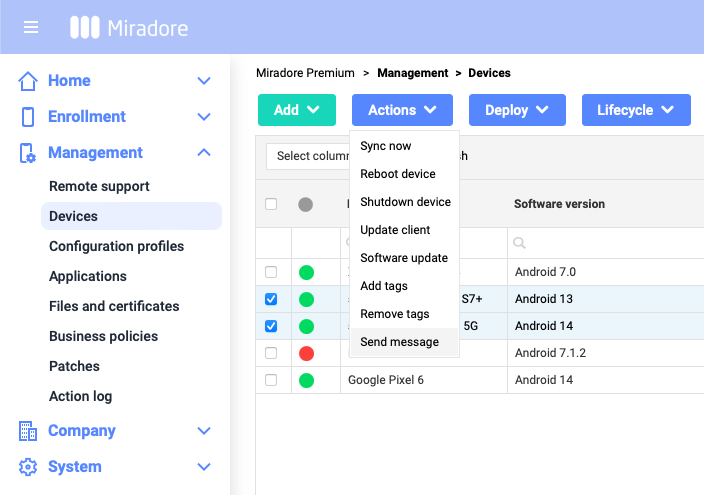
Source: Miradore
9. Scalefusion
Scalefusion is an MDM solution that offers unified endpoint management across Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux, and ChromeOS. It enables device enrollment, strict policy enforcement, and security controls through a single platform.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform support: Unified management for Android, iOS/iPadOS, Windows, macOS, Linux, and ChromeOS devices
- Seamless enrollment: Supports OOBE protocols and low-touch onboarding for BYOD and corporate-owned devices
- Policy enforcement: Lock down device usage with robust policy control, including MDM kiosk modes for single or multi-app environments
- Kiosk mode: Transform devices into dedicated tools with locked-down app access, kiosk browsers, and hardware control
- Application management: Push, update, and restrict public and private apps for maximum productivity and control
Source: Scalefusion
10. SOTI MobiControl

SOTI MobiControl is an enterprise mobility management (EMM) solution to provide visibility and control over mobile devices, IoT endpoints, and other business-critical hardware across major operating systems, including Android, iOS, macOS, Windows, and Linux. It enables organizations to deploy, configure, secure, and monitor devices throughout their lifecycle.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform support: Manages Android, iOS, macOS, Windows, and Linux devices, including legacy hardware and IoT endpoints
- Full lifecycle management: Covers enrollment, configuration, app deployment, policy enforcement, OS updates, and decommissioning
- SOTI XTreme technology: Accelerates app and data delivery by up to 10X, reducing deployment times across remote sites and large device fleets
- SOTI XTreme hub: Optimizes bandwidth usage by routing updates to multiple devices through a single local hub, cutting down repetitive transfers
- Secure device management: Enforces strong passwords, manages firewalls, blocks USB access, and protects against phishing and unauthorized access
Source: SOTI
Considerations for Choosing Mobile Device Management Solutions
While MDM platforms are widely used, many of their foundational assumptions do not align with the needs of modern organizations, especially those embracing BYOD, hybrid work, and decentralized IT. Choosing an MDM solution often means accepting significant trade-offs in cost, complexity, privacy, and user experience:
- Challenges in BYOD environments: MDM platforms rely on full-device control, which is intrusive for employees using personal devices. This model creates friction and privacy concerns, leading to low adoption and enforcement challenges. Attempting to manage both personal and corporate data on the same device introduces legal, technical, and ethical complications.
- Operational overhead: Effective MDM requires continuous configuration, policy tuning, and maintenance of enrollment workflows, compliance settings, and device groups. IT teams must also deal with platform fragmentation—supporting varied operating systems, hardware types, and use cases—all while responding to updates from mobile OS vendors. This adds ongoing complexity and consumes valuable IT resources.
- Inconsistent user experience: MDM policies can interfere with native device features, leading to degraded performance, blocked apps, or restrictions that frustrate users. Remote troubleshooting, while useful, often falls short in real-world scenarios due to limited diagnostic data or inconsistent support across device types and OS versions.
- Scalability issues: As organizations scale, managing large fleets of devices through MDM becomes increasingly difficult. Enrollment processes break down, compliance gaps widen, and policy updates take longer to propagate across distributed teams. Even cloud-based MDM platforms require careful planning and monitoring to avoid bottlenecks and misconfigurations.
- Poor fit for application-centric models: MDM tools are designed around securing devices—not applications or data directly. In environments where the focus is on secure access to business applications and services rather than managing the device itself, MDM adds unnecessary overhead. It does little to protect data movement across unmanaged applications or user actions outside corporate control.
Modern security models, such as workspace isolation, app-level controls, and zero trust access, offer more practical, scalable solutions for today’s workforce. Tools like Venn shift control away from the device and toward the data and applications, reducing administrative overhead while respecting user privacy and maintaining strong security controls. These alternatives better align with hybrid work, contractor access, and BYOD needs without the heavy footprint of traditional MDM platforms.