Top 12 Intune Alternatives for the BYOD Era [2026 Guide]

What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution that helps organizations manage and secure devices, applications, and data. It integrates tightly with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, providing IT administrators with tools to configure security policies, enforce compliance, and manage both corporate and bring-your-own devices (BYOD) across platforms like Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android.
The platform enables businesses to protect corporate information by restricting access to resources based on device compliance and user identity. Intune leverages integration with Azure Active Directory and Microsoft’s security offerings, making it particularly appealing to organizations committed to Microsoft environments. Its ability to streamline device lifecycle management, automate software deployments, and ensure regulatory compliance places it at the core of many enterprise mobility and security strategies.
Top Microsoft Intune alternatives include BYOD protection solutions like Venn and endpoint management solutions like Atera and NinjaOne.
Secure the Data, Not the Device
Protect company data on unmanaged laptops without locking down the entire device.

In this article:
- Key Microsoft Intune Limitations
- Is Microsoft Intune Suitable for Modern BYOD Environments?
- Secure Remote Work Platforms as a Modern Alternative to Intune
- Microsoft Intune Alternatives: Remote Work Platforms
- Should You Consider BYOD Protection Solutions as a Microsoft Intune Alternative? Key Considerations
Key Microsoft Intune Limitations
While Microsoft Intune offers robust capabilities for device and application management, there are several limitations that organizations should be aware of before adopting or scaling its use. These limitations were reported by users on the G2 platform.
- Complex user interface: The Intune console can be difficult to navigate for new administrators. Its extensive options and nested settings increase the complexity of setup and daily management.
- Steep learning curve: Understanding the full range of Intune’s features takes time. Without proper training or documentation, administrators may struggle to configure policies correctly, especially in hybrid environments.
- Slow policy and app synchronization: Policies and application deployments do not always sync promptly. This delay can hinder timely updates or troubleshooting, particularly when managing large numbers of devices.
- Limited application deployment flexibility: Deploying applications that are not in the Microsoft Store can be challenging. Customization options for app deployment are also limited in certain scenarios.
- High cost for small to midsize businesses: Licensing costs can be a barrier for smaller organizations, especially when higher-tier features require additional investment.
- Single-user console access limitation: Currently, the console does not support multiple concurrent users, which can limit collaboration or parallel management tasks.
- Device migration challenges: Transferring data between devices during handset replacements can be slow and cumbersome, impacting user experience.
- Lag in system feedback and logs: System logs and deployment feedback often take time to update, delaying issue detection and response.
- Inconsistent integration with SCCM: Software deployment via SCCM integration could be more seamless. Current integration may create inefficiencies for organizations using both platforms.
- Frequent UI and feature changes: Microsoft’s tendency to rebrand or reorganize features forces administrators to constantly relearn parts of the system.
Is Microsoft Intune Suitable for Modern BYOD Environments?
Microsoft Intune offers a broad set of features that support bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, but its suitability depends on an organization’s specific needs and constraints. Intune supports both mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM), allowing IT administrators to manage devices directly or control access to corporate apps and data without enrolling the entire device. This is useful in BYOD scenarios where users may not want full device oversight by the organization.
However, Intune’s BYOD experience can be limited by user consent and device enrollment friction. Many users are reluctant to enroll personal devices due to privacy concerns, particularly when MDM is required. While MAM with app protection policies can address this by securing only the corporate data inside supported apps, this approach is mainly effective with Microsoft 365 applications. Organizations relying on non-Microsoft apps may find these protections harder to extend.
Additionally, the granularity of controls in BYOD settings can be insufficient for nuanced use cases. For example, enforcing compliance policies without full device management is limited, and certain configurations require device enrollment, reducing flexibility. The lack of consistent cross-platform feature parity also creates challenges in managing iOS and Android devices uniformly.
Secure Remote Work Platforms as a Modern Alternative to Intune
While Microsoft Intune is effective in managing endpoints and enforcing compliance, newer secure remote work platforms offer an alternative model better suited to modern hybrid and BYOD workforces. These platforms focus on isolating the work environment from the underlying device, allowing secure access to corporate apps and data without requiring full device management.
These solutions typically offer faster onboarding, minimal user resistance, and fewer support challenges compared to full-scale MDM systems. They are particularly attractive for organizations with large contractor or freelance populations, or where employee-owned devices dominate.
For companies seeking a secure, low-friction approach to remote work and BYOD, secure remote work platforms can complement or replace traditional tools like Intune, depending on the desired level of control and integration with existing infrastructure.
Microsoft Intune Alternatives: Remote Work Platforms
1. Venn

Venn’s Blue Border takes a different path than Intune MDM. Instead of enrolling the entire device, Venn creates a company-controlled Secure Enclave on the user’s laptop, where all data is encrypted and access is managed. Work apps and data run locally inside this protected environment, isolated from any other activity on the device. IT gets the controls required for security and compliance, but only over the enclave — not the user’s personal files, settings, or activity.
This approach removes the source of BYOD friction. With Venn, there is no full-device takeover and no privacy trade-offs. Users keep their laptops the way they like them, while companies get a controlled workspace that safeguards sensitive data and meets regulatory requirements.
Key features include:
- Granular, customizable restrictions: IT teams can define restrictions for copy/paste, download, upload, screenshots, watermarks, and DLP per user.
- Secure Enclave technology: Encrypts and isolates work data on personal Mac or PC computers, both for browser-based and local applications.
- Zero trust architecture: Uses a zero trust approach to secure company data, limiting access based on validation of devices and users.
- Visual separation via Blue Border: Visual cue that distinguishes work vs. personal sessions for users.
- Supports turnkey compliance: Using Venn helps companies maintain compliance on unmanaged Macs with a range of regulatory mandates, including HIPAA, PCI, SOC, SEC, FINRA and more.
To see a demo of Venn, click here.

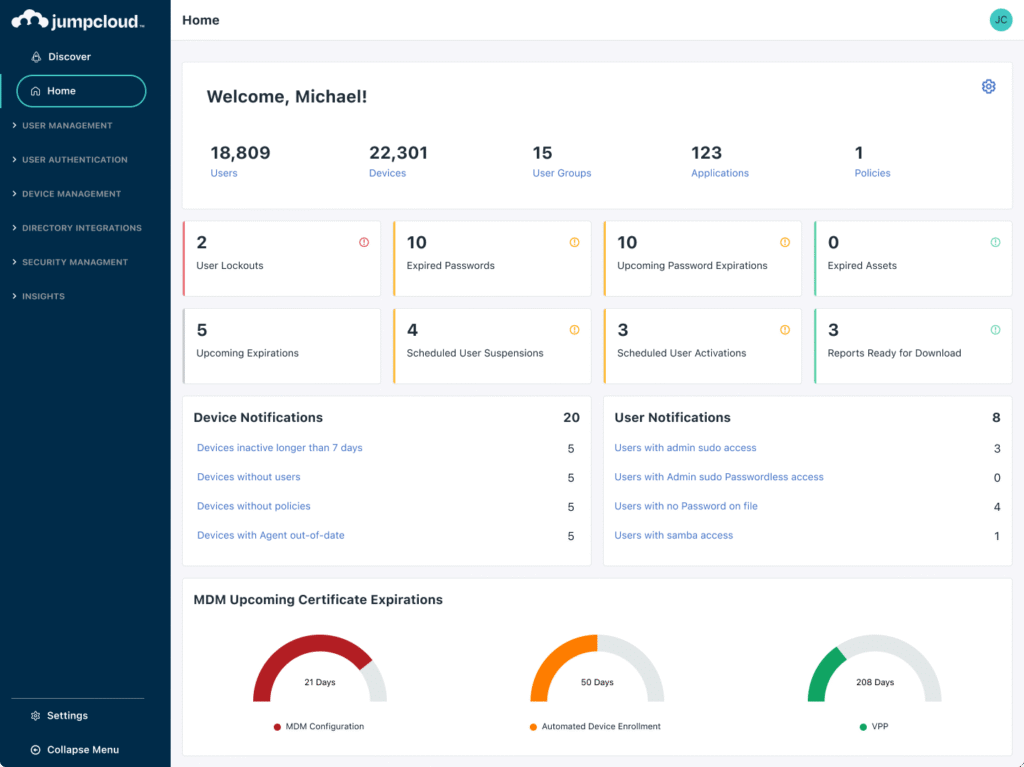
2. JumpCloud Open Cloud Directory

JumpCloud is a cloud-native platform that unifies identity, device, and access management under a single open directory. It enables organizations to manage users, enforce security policies, and provide secure access to applications and devices without the complexity of traditional directory systems.
Key features include:
- Single sign-on (SSO): Offers SAML- and LDAP-based SSO for hundreds of applications, enabling secure, centralized access from a single user portal.
- Conditional access and MFA: Enforces multi-factor authentication at login and supports conditional access policies for added security.
- Cloud directory and identity lifecycle management: Centralized user identity and account provisioning across cloud and on-prem apps using SCIM and JIT.
- Device management: Cross-platform endpoint management with support for Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices.
- Open integrations: Integrates with services like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Okta, and others, allowing flexible stack consolidation.
- Unified dashboard: Admins manage users, devices, access, and policies from a single console for simplified IT operations.
Source: JumpCloud
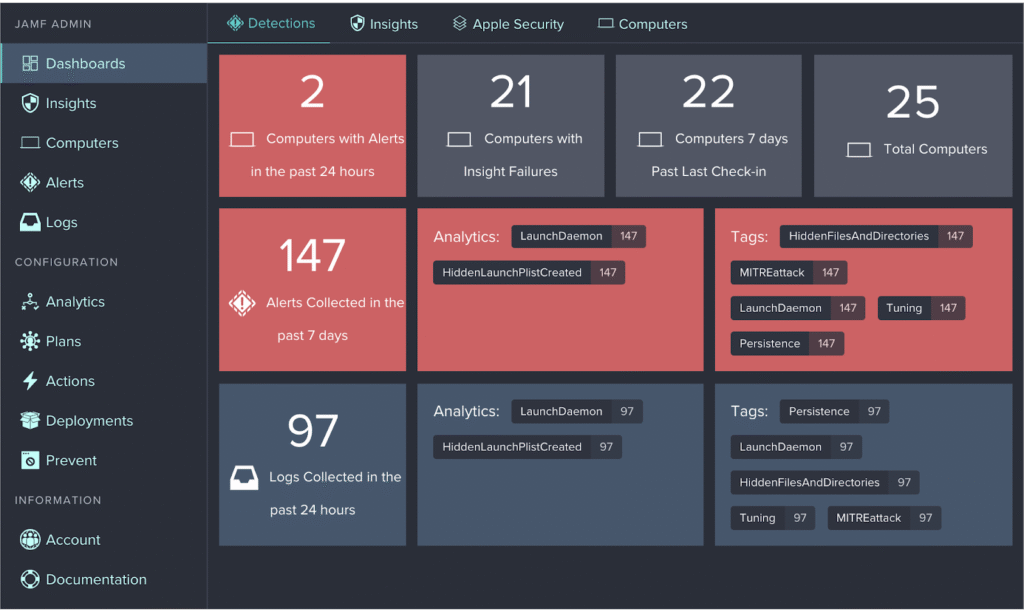
3. Jamf Pro
Jamf Pro is an enterprise-grade mobile device management (MDM) solution for Apple ecosystems. It automates the deployment, management, and security of macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices while preserving the native Apple user experience. Jamf Pro is widely used by organizations that prioritize secure, scalable Apple device management.
Key features include:
- Zero-touch deployment: Automatically provision and configure Apple devices out-of-the-box using Apple Business Manager and Jamf workflows.
- Device and app management: Remotely configure devices, enforce policies, and manage apps across large Apple fleets.
- Security and compliance tools: Includes endpoint protection, threat prevention, content filtering, and visibility into device compliance.
- Inventory and reporting: Tracks hardware, software, and configuration data across all managed devices for audit and planning purposes.
- Self-service portal: Enables users to install approved apps, request resources, and perform common tasks without IT intervention.
- Extensive integrations: Works with major platforms including Microsoft Intune, Google Workspace, Okta, and AWS for simplified IT operations.
Source: JAMF Pro
Microsoft Intune Alternatives: Traditional UEM Solutions
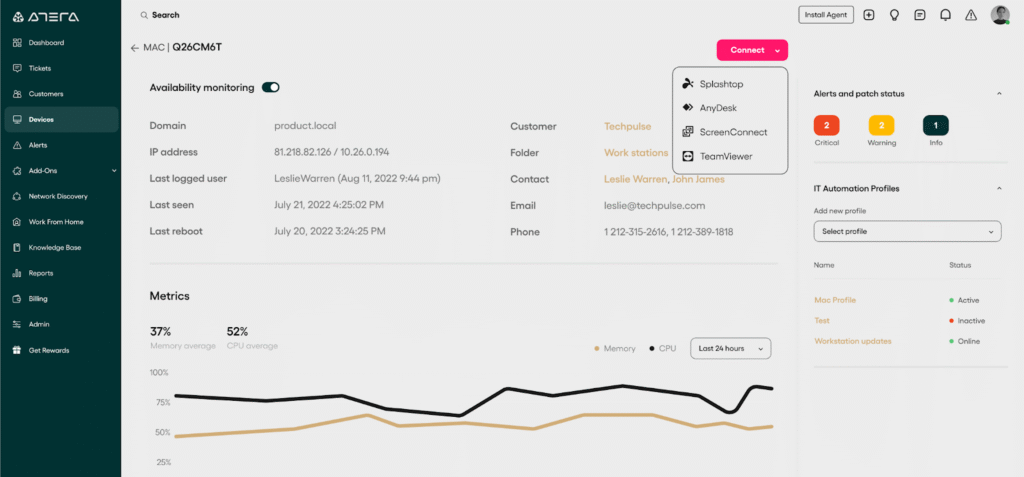
4. Atera RMM

Atera is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform to help IT teams and managed service providers oversee their entire IT environment from a single interface. It provides a solution for endpoint monitoring, patch management, automation, and remote access.
Key features include:
- Remote management: Secure remote access to endpoints using integrated tools such as AnyDesk, TeamViewer, and ScreenConnect
- Patch management: Automate OS and software patching to maintain security and compliance
- IT automation: Script and schedule routine tasks to reduce manual workload
- Network monitoring: Real-time alerts and monitoring to detect and respond to issues quickly
- Software management: Deploy and manage software across devices from a centralized console
Source; Atera RMM
5. NinjaOne

NinjaOne is an all-in-one remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform to help managed service providers (MSPs) and IT teams manage endpoint management. It simplifies IT operations through a fast, cloud-native interface and automation tools.
Key features include:
- Real-time monitoring and alerting: Detect and respond to device issues with proactive alerts that reduce downtime
- Automated patching: Patch Windows, macOS, Linux, and over 200 third-party applications with minimal manual intervention
- One-click device actions: Perform tasks like terminal access, service restarts, or software deployment without disrupting users
- Secure remote access: Control endpoints remotely using built-in tools for fast, hands-on support
Source: NinjaOne
6. Hexnode UEM

Hexnode UEM is a unified endpoint management platform that allows IT teams to manage diverse devices, including desktops, mobile phones, rugged hardware, and IoT endpoints, from a single interface. It supports multiple operating systems and form factors, enabling consistent policy enforcement and streamlined operations across the entire device fleet.
Key features include:
- Cross-platform device management: Manage Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and IoT devices in one platform
- Identity and access management: Integrate with identity providers to enforce user access policies across devices and applications
- Automated patch management: Set rules for zero-touch OS and patch updates to keep endpoints secure and current
- Workflow automation: Use triggers and actions to automate complex device management tasks with minimal manual input
- Mobile device management (MDM): Configure, secure, and monitor mobile devices across multiple platforms
Source: Hexnode UEM
7. Ivanti Neurons

Ivanti Neurons is a cloud-native platform built to unify IT and security operations through intelligent automation, integrated analytics, and scalable services. It centralizes device, user, and security data into a single system to improve visibility and streamline workflows.
Key features include:
- Unified platform services: Centralized analytics, automation, and agent management across Ivanti solutions
- Cross-functional visibility: Consolidates data from devices, support operations, and security tools for actionable insights
- Integrated endpoint and security management: Manage and secure endpoints while identifying and addressing exposure risks
- Enterprise service management: Connect IT service workflows with device and security data to improve resolution and service quality
- Cloud-optimized deployment: No infrastructure or upgrades needed
Source: Ivanti Neurons
8. IBM MaaS360

IBM MaaS360 is a cloud-based unified endpoint management (UEM) platform to help organizations securely manage devices, users, apps, and data across a distributed workforce. Powered by AI, MaaS360 simplifies device enrollment, automates policy enforcement, and enhances security across mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and purpose-built devices.
Key features include:
- Unified endpoint management: Manage mobile devices, laptops, and special-purpose endpoints from a centralized console
- Fast start setup: Deployment tailored for small and mid-sized businesses with built-in protection and automation
- AI-driven security and insights: Detect threats and gain visibility across endpoints using AI-powered analytics
- Automated device and policy management: Enforce security policies and manage device settings automatically to reduce manual effort
- Industry-specific solutions: Supports compliance and use cases across sectors like healthcare (HIPAA), financial services, retail, and logistics
Source: IBM MaaS360
9. ManageEngine Endpoint Central

ManageEngine Endpoint Central is a unified endpoint management (UEM) platform that combines IT operations and security into a single solution. It enables IT teams to manage, secure, and support desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and servers across hybrid and distributed environments.
Key features include:
- Automated patching: Automatically deploy patches for Windows, macOS, Linux, and third-party applications to reduce vulnerabilities
- Asset management: Track hardware and software assets, monitor usage, and manage licenses and warranties
- Threat detection and remediation: Identify and fix security issues in real time with compliance support for over 75 CIS benchmarks
- Ransomware protection: Detect root causes of attacks and provide rapid response to contain and prevent future threats
- Mobile device management (MDM): Centralize mobile device, app, email, and content management with compliance controls
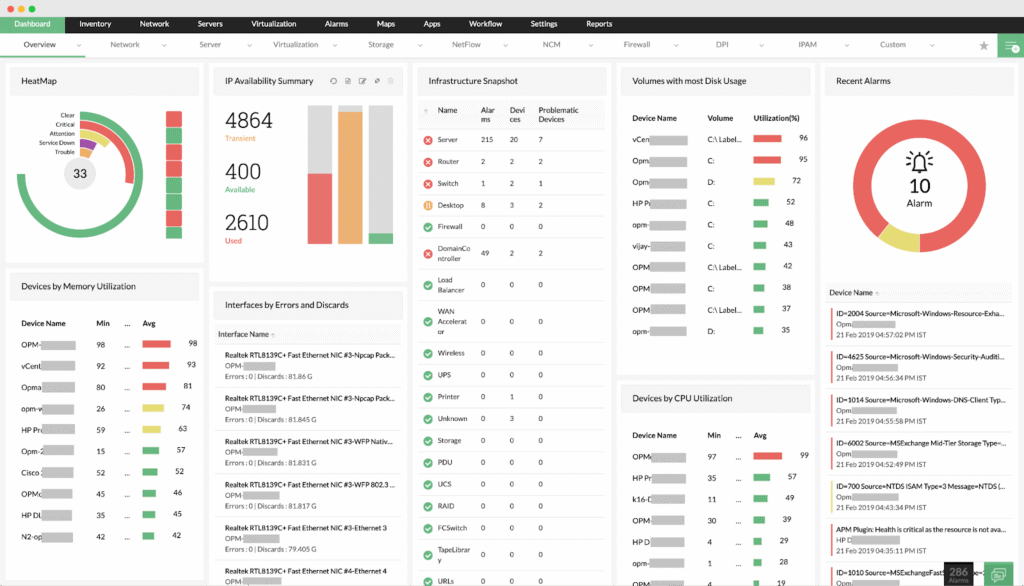
Source: ManageEngine
10. N-able N-sight

N-able N-sight is a unified endpoint management solution designed for simplicity, speed, and scalability. It combines remote monitoring, security, automation, and support tools into a single platform for managing Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and network devices.
Key features include:
- Remote monitoring and management: Full device monitoring, alerting, and control across multiple operating systems
- Vulnerability management: Identify and remediate security exposures quickly with built-in scanning and prioritization
- Automated patch management: Fast, policy-driven patch deployment for OS and third-party applications
- Drag-and-drop automation: 650+ ready-to-use scripts and policies with no-code automation tools for scale and speed
- Secure remote access: Offer attended or unattended support with live chat, file transfer, and remote control
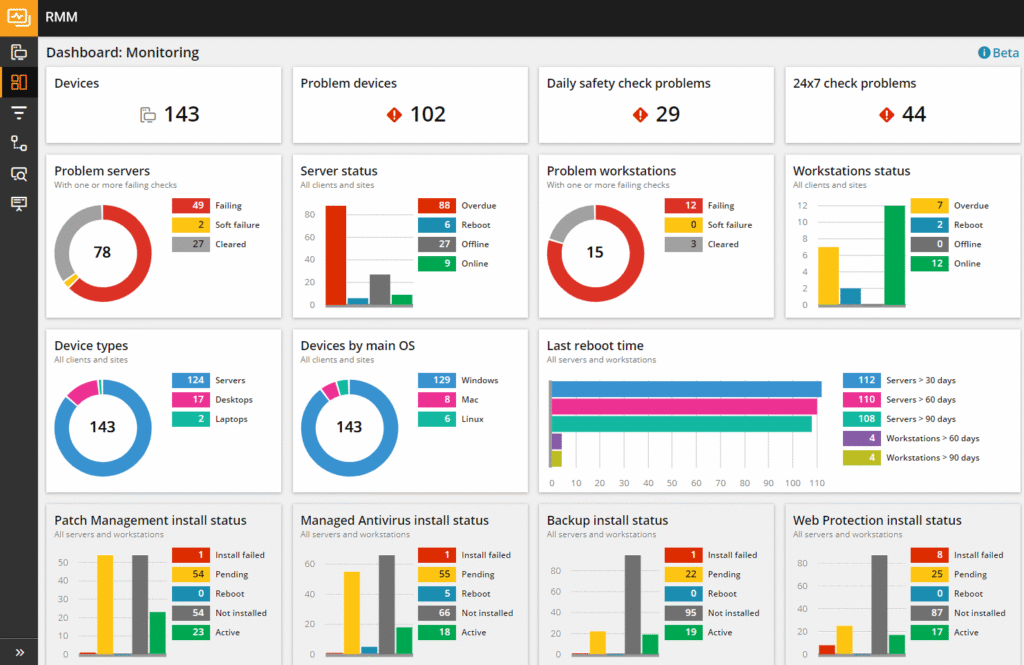
Source: N-Able N-Sight
11. ConnectWise Automate

ConnectWise Automate is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform built for MSPs that need high levels of customization, visibility, and automation across their endpoint environments.
Key features include:
- Granular endpoint management: Monitor and manage every endpoint with customizable roles, policies, and workflows
- Advanced automation and scripting: Use prebuilt or AI-assisted PowerShell scripts to automate remediations at scale
- Patch management: Standardize Windows patching with approval policies, deployment rings, and exception tracking
- Deep visibility with data views: Search, filter, and export real-time insights into software, configurations, and compliance
- Remote support tools: Perform background maintenance and resolve issues across platforms without disrupting users
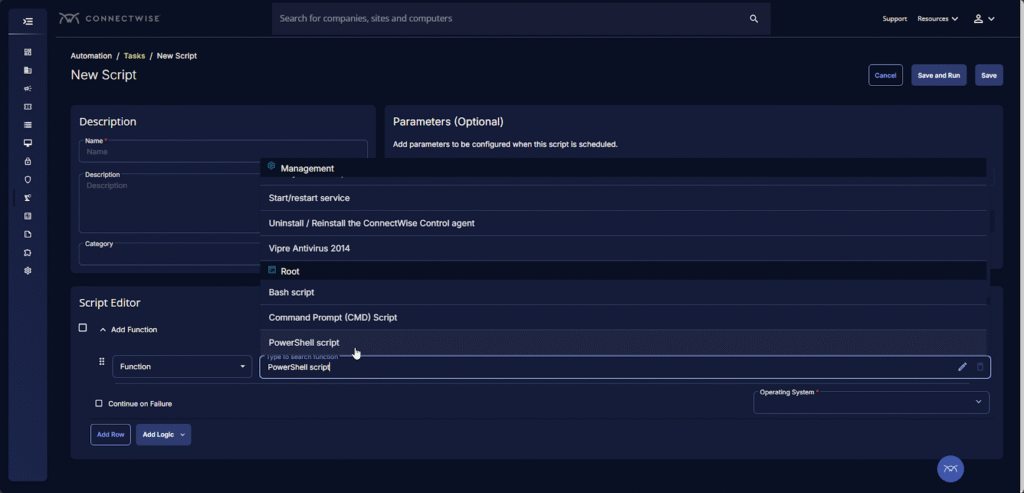
Source: ConnectWise
12. Workspace ONE
Workspace ONE is a cloud-native unified endpoint management (UEM) platform that enables organizations to manage and secure any device, across any ownership model, from a single console. It supports corporate-owned, BYOD, shared, and mission-critical devices.
Key features include:
- Unified endpoint management: Manage all devices, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, under a single platform
- Zero trust security: Enforce conditional access and compliance checks before granting resource access; auto-remediate or wipe non-compliant devices
- Remote onboarding: Enable zero-touch provisioning without imaging, allowing users to set up corporate devices from anywhere
- IT orchestration and automation: Use a low-/no-code interface to automate complex IT tasks and reduce manual effort
- Lifecycle app management: Deliver and manage apps across all platforms, with single sign-on (SSO) and a unified app catalog via Intelligent Hub
Source: Workspace ONE
Should You Consider BYOD Protection Solutions as a Microsoft Intune Alternative? Key Considerations
When evaluating whether to stay with Microsoft Intune or move to a modern secure remote work platform, the decision largely depends on your organization’s device ownership model, security needs, user experience goals, and IT resource constraints. Unified endpoint management (UEM) platforms like Intune offer comprehensive control, but that control often comes at the cost of user privacy, onboarding complexity, and support overhead, especially in bring-your-own-device (BYOD) environments.
Key considerations include:
- User privacy and device control: UEM tools like Intune often require mobile device management (MDM) enrollment to enforce security policies. This gives IT teams deep control over devices but can create user resistance, particularly for employees using personal devices. BYOD protection platforms, by contrast, focus on isolating work environments without managing the entire device. This preserves user privacy while still protecting corporate data, making adoption easier and minimizing friction.
- App and data isolation: BYOD protection platforms use technologies such as local workspace containers or encrypted zones to separate business apps and data from personal use. This provides strong data protection without device-wide oversight. Intune supports mobile application management (MAM) with app protection policies, but these are mostly limited to Microsoft 365 apps. If your workflows rely on third-party or custom apps, a platform purpose-built for secure BYOD may offer more flexibility.
- Onboarding and deployment speed: UEM tools generally require configuration profiles, compliance policies, and app deployment steps that can delay onboarding. Secure BYOD platforms often use lightweight clients or containerized environments that users can activate quickly, reducing setup time and IT support burden, especially helpful for contractors or temporary workers.
- Cross-platform consistency: Managing policies across iOS, Android, and other platforms can be inconsistent with UEMs like Intune. Many BYOD solutions are designed from the ground up to deliver uniform experiences across operating systems, which simplifies policy enforcement and improves the user experience across device types.
- Licensing and cost considerations: UEM platforms may require higher licensing tiers for advanced features, which can be cost-prohibitive for small and mid-sized businesses. BYOD protection platforms often offer simpler pricing models and better cost alignment for organizations that don’t need full device lifecycle management.
- Regulatory and security requirements: If your organization operates in a highly regulated industry, a UEM may still be necessary for full device control and audit capabilities. However, many BYOD platforms now meet stringent compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, SOC 2) through secure workspaces and data handling policies—without needing to manage the full device.
Learn more in our detailed guide to Intune BYOD
Venn: Ultimate Intune Alternative for BYOD
Venn’s Blue Border secures company data on BYOD laptops without taking over the entire device. Work apps and data run in an encrypted, company-controlled secure enclave, isolated from personal activity. IT gets full control over corporate data, while users keep their personal files and settings. With zero trust access, customizable restrictions, and built-in compliance support, Venn protects sensitive information without compromising privacy or user experience, making it a great Intune alternative for BYOD.